Remote Spooling Communications Subsystem (RSCS) Networking Program Product
The RemoteSpooling Communications Subsystem Networking program product (Program Number 5748-XP1) is the successor to the current RSCS component
ofVM/370 and the VM/370 Networking (VNET) programming PRPO P09007 (Program Number 5799-ATAj. The ases Networking prcgram product provides
Remote Job Entry into aVM/370 system and allows a VM/370 system to
participate in a network of computer systems that use the Network Job
Interface/Network Job Entry (NJI/NJE) protocol.
Phased migration to theRSCS Networking program product is possible
becauseRSCS Networking is a superset of either the RSCS component of V8/370 or the VNET PRPQ. RSCS Networking is compatible with both of
these facilities, except that theRSCS operator will see minor parameter
incompatibilities in the TRACE,CMD commands. The RSCS Networking program product can coexist on with the RSCS component of VM/370 Release 6 provided that each has its own
separateDASD space.
For more detailed information on theRSCS Networking program product,
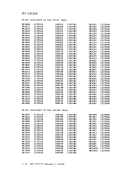
refer to the following list of publications:GH24-5004 General Information Manual SH24-5005 Program Reference and Operations Manual LY24-5203 Logic Manual 5124-5119 Reference Summary Card SRL PUBLICATIONS The following publications contain information on the RSCS Networking
program product:GC20-1800 Introduction GC20-1801 GC20-1807 System Programmer's Guide Section 1. Summary of Changes to the VM/370 system 1-21
The Remote
of
Remote Job Entry into a
participate in a network of computer systems that use the Network Job
Interface/Network Job Entry (NJI/NJE) protocol.
Phased migration to the
because
these facilities, except that the
incompatibilities in the TRACE,
separate
For more detailed information on the
refer to the following list of publications:
program product: