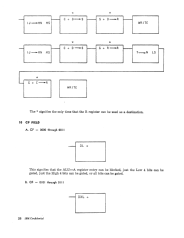
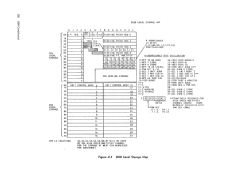
*CD--4 Bits
*CF-3 Bits
*CG-2 Bits
*CV-2 Bits
*CC-3 Bits
#
*CS-4 Bits
*AS-I Bit
*PC-I Bit
Destination from Z buss
Controls the Hi/Lo, crossed/straight functions of the A register entry into
theALU
Controls the Hi/Lo functions of the B regisi;er entry into the AL U
True/complement and Binary/decimal controls
Carry control and logic control
Status control
Alternate CS decoder bit
Odd parity on control registers
#-Fields with alternate decoders
*-Fields with control register
Control Field (Detailed Explanations)
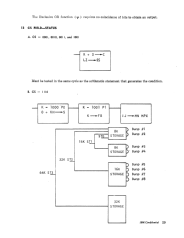
CN Field
PN Field
PA Field
CH and CL Fields
2
IBM Confidential
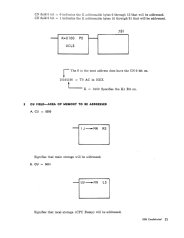
The high order 6 bits of the ROS address register X are loaded from the
CN field.
Provides odd parity on CN for generating parity on X when the other two
bits of X are known.
Provides a check on the word read from ROS.
It
is odd parity on the 12 bit
address WX.
These fields handle the branching of the ROS address. The CH field con-
trols the X register 6 bit in the ROS address register, and the CL field con-
trols the X register 7 bit. All conditions must be set before the cycle in
which the branch is interrogated.
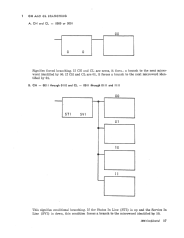
CH
=
0000 or 000 I
In this condition the constants are used for forced branching. CH
=
0000
forces the X register 6 bit off (0), and CH
=
0001 forces the X register 6
bit on (1). (See example lA, page 17.)
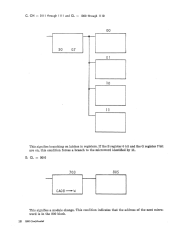
CH = 0010 (RO)
This is a branch on a latch in the R register.
If
the R register 0 bit is a 1,
the X register 6 bit is forced on (1), satisfying the branch condition.
CH
=
0011 (V67
=
0) (GMWM-If 1401 feature)
This is a conditional branch.
If
the V register 6 and 7 bits are 0, the X reg-
ister 6 bit is forced on (1), satisfying the branch condition. The GMWM,
if a 1401 feature, is a conditional branch. (See example 1B, page 17.)
CH
~
0100 (STI)
This is a conditional branch. If the status-in-line (Multiplex Channel) for
the interface is up, the X register 6 bit is forced on (1) satisfying the
branch condition. (See example IB, page 17.)
CH = 0101 (OPI)
This is a conditional branch.
If
the operational-in-line (Multiplex Channel)
for the interface is up, the X register 6 bit is forced on (1), satisfying the
branch condition. (See example IB, page 17.)
CH = 0110 (AC)
This is a conditional branch. If an adder carry resulted in the previous
cycle, the X register 6 bit if forced on (1), satisfying the branch condition.
(See example 1B, page 17.)