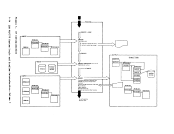
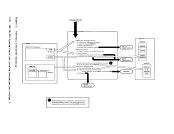
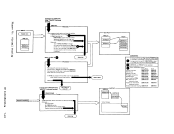
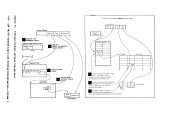
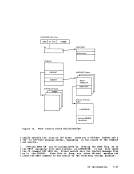
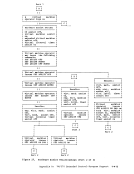
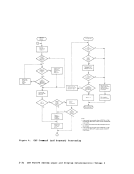
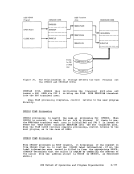
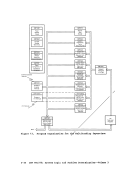
indicates how control is passed to
processes the STRINIT macro. Since
nucleus-resident routine, other nucleus-resident routines can
branch directly to it (
not nucleus-resident must use linkage
operands are specified, the default is
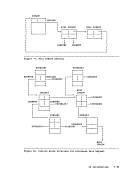
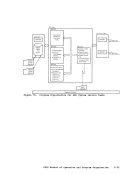
initialized to the end of the user's program, in the user program area.
As storage is allocated from the user program area to satisfy GET
are always in multiples of doublewords, so that this pointer is always
on a doubleword boundary. As the allocated storage is released, the
The pointer
If a
insufficient storage is available to satisfy the request.
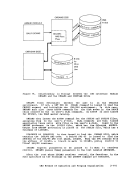
The area between
that are not allocated and that are, therefore, available for allocation
by a
first one pointed to by the
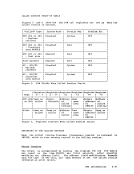
for a description of
The format of an element on the
follows:
o (0)
4 (4)
reserved for
additional reserved pages (for example, for larger directories) should
free up some of the variable