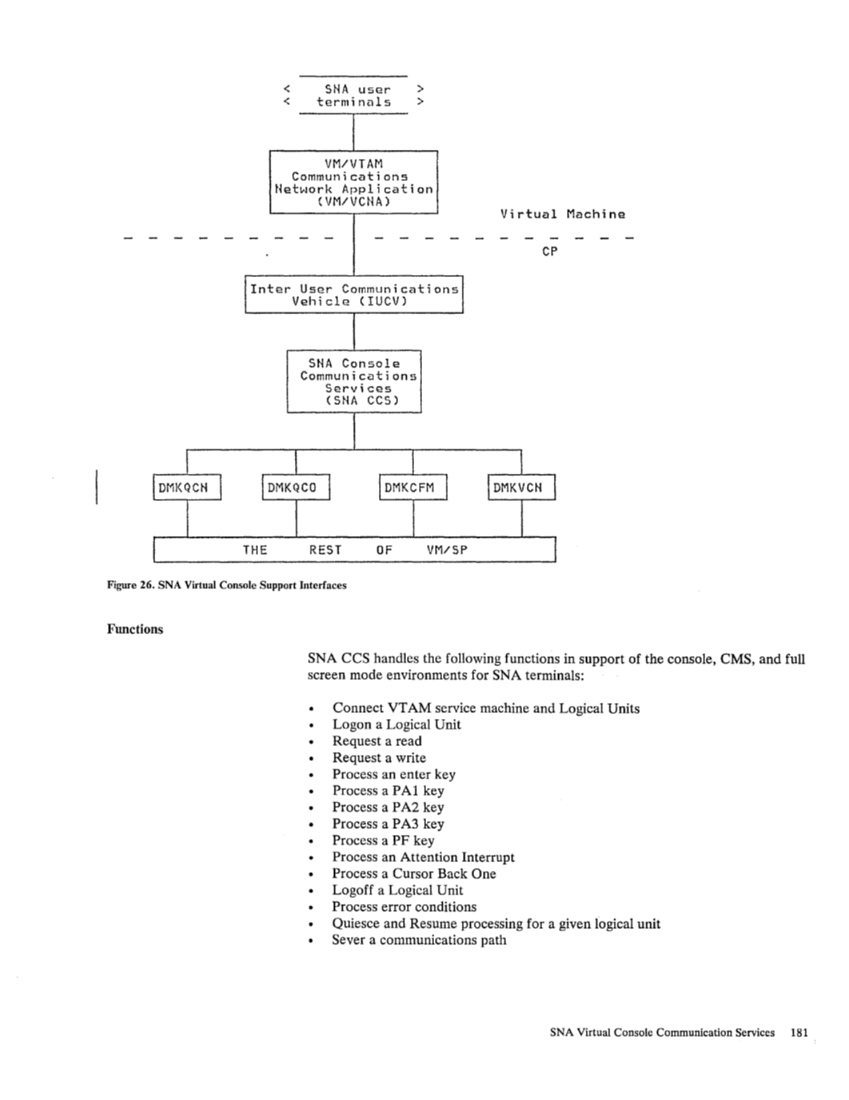
<
<SNA user terminuls >
>
VM/VTAMCommunications Network Application
(VM/VCNA)
Inter User Communications
Vehicle (IUCV)
THESNA Console Communications
Services(SNA CCS) REST OF VM/SP Virtual Machine CP Figure 26. SNA Virtual Console Support Interfaces
Functions
SNA CCS handles the following functions in support of the console, CMS, and full
screen mode environments for SNA terminals:
Connect VTAM service machine and Logical Units
Logon a Logical Unit
Request a read
Request a writeProcess an enter key Process a PAl key Process a P A2 key Process a P A3 key Process a PF key Process an Attention Interrupt Process a Cursor Back One Logoff a Logical Unit Process error conditions
Quiesce and Resume processing for a given logical unit
Sever a communications path
SNA Virtual Console Communication Services 181
<
>
VM/VTAM
(VM/VCNA)
Inter User Communications
Vehicle (IUCV)
THE
Services
Functions
SNA CCS handles the following functions in support of the console, CMS, and full
screen mode environments for SNA terminals:
Connect VTAM service machine and Logical Units
Logon a Logical Unit
Request a read
Request a write
Quiesce and Resume processing for a given logical unit
Sever a communications path
SNA Virtual Console Communication Services 181