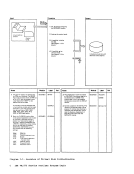
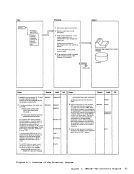
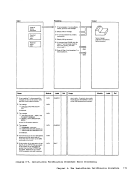
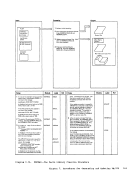
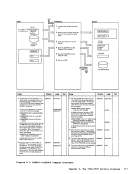
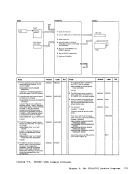
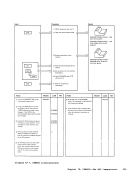
Input I r:::l
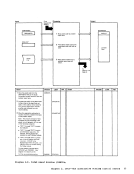
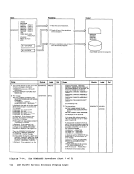
1 Attempt a read toNUC MAP A 1.
Note: The nucleusload map is assumed
to reside on theIPCS user's A-disk. If NUC MAP A 1 cannot be found, issue
message:
UNABLETO LOCATE NUCMAPA1 Follow this message with message:
ENTER fn ft fnOF THE
NUCLEUSLOAD MAP If the load map is successfully located, compare the address of the
constant DMKCPEND in thesymbol table (dump record 1) to the address
of DMKCPEND in theload map. If the addresses do not compare, issue
message:
NUCLEUS MAPINVALID 'file id' If the map is valid, read each line of
the map into a buffer.If it contains
amodule or entry point name, move
this name and associated address(12 bytesl to 3:l output buffer
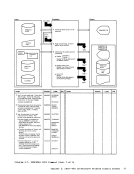
2 Whenend-of-file is reached sort
the output buffer by ascending
entry point address, write the
output buffer and append it to
the dumpfile. I From
Diagram 2-5
(Step 2)
Module
DMMAP
Processing
Extract themodule name
entry points andinitially loaded address for each CP nucleus module. 2 Append the compressed map
to the dumpfile. Label Ref Notes
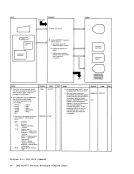
READ
READERR
STATERRI I MAPNAME XCK MAPERROR
READWRTOUT To
Diagram 2-5
(Step 3)Output I o DMMMAP8071 DMMMAP806R
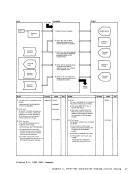
DMMMAP808LOutput Buffer r-::\ I Ref I I Diagram 2-6. Compress the Nucleus Load Map Chapter 2. IPCS--The Interactive preble. Centrel system 31
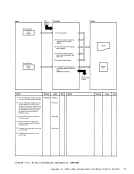
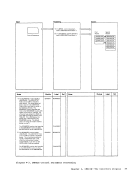
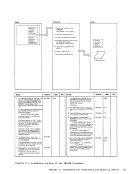
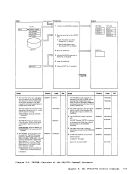
1 Attempt a read to
Note: The nucleus
to reside on the
message:
UNABLE
ENTER fn ft fn
NUCLEUS
constant DMKCPEND in the
of DMKCPEND in the
message:
NUCLEUS MAP
the map into a buffer.
a
this name and associated address
2 When
the output buffer by ascending
entry point address, write the
output buffer and append it to
the dump
Diagram 2-5
(Step 2)
Module
DMMAP
Processing
Extract the
entry points and
to the dump
READ
READERR
STATERR
READ
Diagram 2-5
(Step 3)
DMMMAP808L