March 30, 1979
Restrictions on the use of access method services andVSAM under OS and DOS users are listed in CMS and eMS/DOS command formats, operand-descriptions, and responses for each of the commands described
here.When you are going to execute VSAM programs in CMS or CMS/DOS, you
should remember to issue the DLBL command to identify the master
catalog, as well as any other program input or output file you need to
define.
Using the AMSERV Command
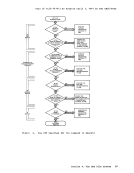
InCMS, you execute access method services utility programs with the AMSERV command, which has the basic format:
amserv filename
"filename" is the name of aCMS file that contains the control
statements for access method services.!gte: Throughout the remainder of this section the term "lMSERV" is used
to refer to both theCMS AMSERV command and the OS/VS or DOS/VS access
method services, except where a distinction is being made betweenCMS and access method services. You create an AMSERV file with the CMS editor using a filetype of AMSERV and any filename you want; for example:
edit lIastcat amservNEW FILE:
EDIT:
input
The editor recognizes the filetype ofAMSERV and so automatically sets
the margins for your input lines at columns 2 and 72.The sample AMSERV file being created in the example above, MASTClT lMSERV, might contain
the following control statements:
DEFINEMASTERCATALOG (NAME (MYCAT) - VOLUME (123456) CYL (2) -
FILE(IJSYSCT) )
Note that the syntax of the control statements must conform to the rules
for access method services, including continuation characters and
parentheses. The only difference is that theAMSERV file does not
contain a"/*" for a termination indicator.
Before you can execute the DEFINE control statement in thisAMSERV example, you must define the output file, using the ddname IJSYSCT. You can do this using the DLBL command. Since the exact form required in
the DLBL command varies according to whetherJOU are an OS or a DOS user, separate discussions of the DLBL command are provided later in
this section. All of the following examples assume that any disk data
set or file that you are referencing with anAMSERV command will have
been defined by a DLBL command.When you execute the AMSERV command, the AMSERV control statement
file can be on any accessedCMS disk; you do not need to specify the
filemode and, if you are aDOS user, you do not need to assign SYSIPT. The task of locating the file and passing it to access method services
is performed byCMS. 182 IBM VM/370 eMS User's Guide
Restrictions on the use of access method services and
here.
should remember to issue the DLBL command to identify the master
catalog, as well as any other program input or output file you need to
define.
Using the AMSERV Command
In
amserv filename
"filename" is the name of a
statements for access method services.
to refer to both the
method services, except where a distinction is being made between
edit lIastcat amserv
EDIT:
input
The editor recognizes the filetype of
the margins for your input lines at columns 2 and 72.
the following control statements:
DEFINE
FILE
Note that the syntax of the control statements must conform to the rules
for access method services, including continuation characters and
parentheses. The only difference is that the
contain a
Before you can execute the DEFINE control statement in this
the DLBL command varies according to whether
this section. All of the following examples assume that any disk data
set or file that you are referencing with an
been defined by a DLBL command.
file can be on any accessed
filemode and, if you are a
is performed by