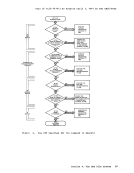
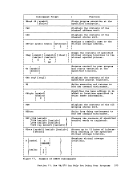
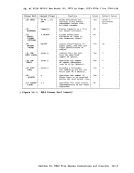
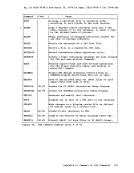
r
dlbl newfile b (extent
r
(null line)
If you make any errors issuing the DLBL
r
IDENTIFYING
of the DLBL command sequence:
dlbl old
r
e
(null line)
the first disk volume on the command line.
remaining extents. In the above example, the data set has extents on
disks accessed as B-, C-,
r
r
valid addresses for tapes are 181, 182, 183, and 184.
tapes, you can also refer to them using their
for the tape device interactively, after you issue the
you issue the
tape for input or
r
specify the tape device being used:
labeldef tapedd fid filename
In this
r
virtual address 181.
output from an
After you enter the ddname
LABELDEF command is required because the
the tape open needs label inforaation for standard labelled tapes.
information. The filename you specify on the LAEELDEF command should be
the same one you use to reply to the access method service message that
requested you to supply the tape's ddnames. However, the
tape labels skipped, but not checked, enter a LABELDEF with no
parameters other than filename.