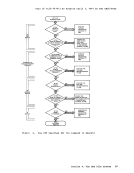
that is necessary, and
space.
the extents you specify to see whether they are greater than the number
of cylinders available.
cylinder number and the extents you specify are on cylinder boundaries,
the DEFINE function completes successfully. However,
error message when you use an
space.
To define a cluster for
need (1) an
defining the cluster, and (2) the
catalog) volume, which will point to the cluster. The
the cluster is to reside does not have to be online when you define a
suballocated cluster.
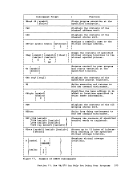
For
DEFINE
FILE
DATA
To execute this file, you would need to enter the following
virtual machine at address
DLBL
reside must be mounted and accessed when you execute the
portions separately.
To execute an
(the ellipses indicate that the