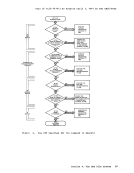
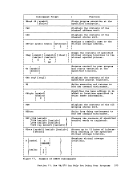
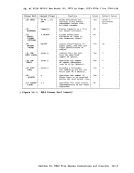
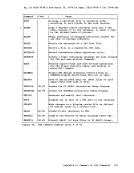
and filetype following the keyword
dlbl outfile a
the output is written to your
enter:
dlbl outfile a ems
the DLBL
To clear all
dlbl * clear
This command is issued
they
program, the DLBL definitions in effect are cleared, including those
entered
the DLBL
dlbl
or, you can use the
Using
fro.
the terminal, or print:
using the