42 IBM VM/370 eMS User's Guide
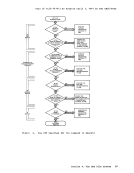
The file is the essential unit of data in the
files are unique to the
other operating systems.
using a file identifier. The file identifier consists of three fields:
reference files, you must identify the file by using these fields.
filetype; others require
section contains information about the things you must consider when you
give your
that create and modify
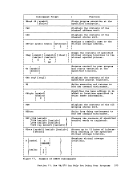
The
physical blocks; regardless of whether they have fixed-or
variable-length records. For most of your
need to specify either a logical record length and record format or
block size when you create a
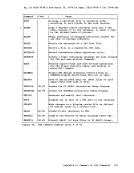
default characteristics, based on its filetype. The special filetypes
recognized
written by
systems. you cannot, however, use any
and write
the same format as
recognized by those operating
file formats are unique to the
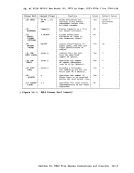
For a mini disk formatted in
65,533 logical records, all of which must be on the same minidisk. If
the file is a source program, the file size limit may be smaller. The
maximum number of files per real disk in the
format is
or 2319.
For a minidisk formatted in
blocks, a single
31
-
blocks of data, grouped into as many as 2
31
-1 logical records, all of
which must be on the same minidisk. The approximate limits to the
number of files per disk, expressed in thousands, are: