April 1, 1981
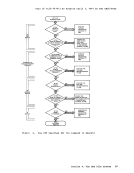
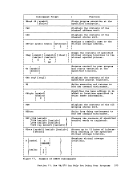
If thereare files named MYFILE ASSEMBLE on your A-disk and C-disk, then only your A-disk is displayed. The commands that perform
this type of search are:DISK DUMP EDIT
FILEDEFPRINT PUNCH RUN SORT STATE SYNONYM TAPE DUMP TYPE For the COMPARF, COPYFILE, RENAME, and SORT commands, you must always
specifya filemode letter, even if it is specified as an asterisk. WHEN TO FILEMODE LETTERS: WRITING FILES When you issue a CMS command that writes a file onto one of your virtual lnd you specify the output filemode, CMS writes the file onto
thatdi3K.
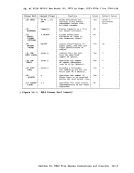
are:COPYFILE RENAME SORT The commands that allow you to specifv,the output filemode, but do
notrequire it, are:
FILEDEFLOAD TApoDS UPDATE When VOl do not specify the filemode on these commands, :MS writes the
outout files onto your A-disk.Same A-disK. The INCLUDE commands write a file named LOAD MAP AS.
The LIsrFILE command creates a file namedCMS EXEC, on your A-disk. The CMS/DOS commands DSERV, ESERV, SSEFV, PSERV, and RSERV also write files
onto your A-disk.Other
outputriles either: • To the disk from which the input file was read, or • Ta A-disk, if the file was read from a read-only disk
These commands are:MA:LIB TXTLIB
filemode as anasterisK (*).
Inlddition, many of the lanquage processors, when creating worK files and permanent files, write onto the first read/write disk in your
searchard9r, if they cannot write on the source file's disk or its
parent.54 IBM VM/370 eMs User's Guide
If there
this type of search are:
FILEDEF
specify
that
are:
not
FILEDEF
outout files onto your A-disk.
The LIsrFILE command creates a file named
onto your A-disk.
output
These commands are:
filemode as an
In
search
parent.