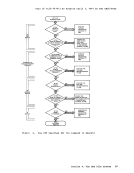
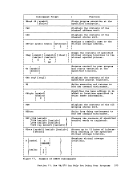
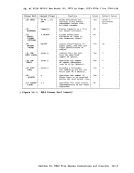
RENAME or
the edit environment.
programs or
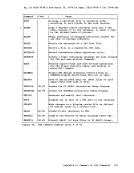
To change the filemode number of an
READCARD:
RENAME:
fileids on the
Managing Your
The number of files you can write on a
of the disk and the size of the files that it contains.
out how
enter:
query disk a
The response may be something like this:
LABEL cuu
longer need.
to keep active on disk.
disk, and the disk becomes full in the process, you receive an error
message, and you have to try to clear some space on the disk before you
can attempt to execute the command or program again. To avoid the
delays that such situations cause, you should try to maintain an
awareness of the usage of your disks. If you cannot erase any more
files from your disks, you should contact installation support personnel
about obtaining additional read/write
Each
of the
the
into a user file directory. The user file directory has an entry for
each file that you may access. If you have accessed a disk specifying
only particular files, then the user file directory contains entries
only for those files.
56 IBM