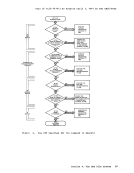
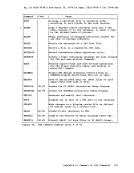
listds d (free
The responsefrom LISTDS might look like this: FREESPACE INFORMATION FOR 'D' DISK: CYL-HD(RELTRK) TO CYL-HD(RELTRK) TRACKS 000 01 1 000 09 9 9 000 11 11 029 18 569 560 From this response, you can see that the volume table of contents (VTOe) is located on the first cylinder, so you can allocate cylinders 1
through 29 forVSAM: assgn syscat c
dlbl ijsysct c dsn mastcat (syscat perm extentDMSDLB331R ENTER EXTENT SPECIFICATIONS: 19 551
(null line)
After entering the extents, in tracks,g1v1ng the relative track number
of the first track to be allocated followed by the number of tracks, youmust enter a null line to complete the command. A null line is required
because, when you enter multiple extents, entries may be placed on more
than one line. If you do not enter a null line, the next line you enter
causes an error, and you must re-enter all of the extent information.
Note that, as inDOS/VS, the extents must be on cylinder boundaries, and
you cannot allocate cylinderO. Now you can issue the AMSERV command:
amserv mastcatA ready message with no return code indicates that the master catalog is
defined.You do not need to reissue the ASSGN and DLBL commands in order
to use the master catalog for additionalA!SERV functions. You can use the AMSERf command to define private catalogs and spaces for
them, also. The procedures for determining what space you can allocate
are the same as those outlined in the example of defining a master
catalog.
For a user catalog, you may use any programmer logical unit, and any
ddname:
access 199 e
listds e (freeaS5gn sys001 e
dlbl cat1 e dsn private cat1(sy5001 extent perm
amserv usercat
192IBM VM/370 CMS User's Guide
The response
through 29 for
dlbl ijsysct c dsn mastcat (syscat perm extent
(null line)
After entering the extents, in tracks,
of the first track to be allocated followed by the number of tracks, you
because, when you enter multiple extents, entries may be placed on more
than one line. If you do not enter a null line, the next line you enter
causes an error, and you must re-enter all of the extent information.
Note that, as in
you cannot allocate cylinder
amserv mastcat
defined.
to use the master catalog for additional
them, also. The procedures for determining what space you can allocate
are the same as those outlined in the example of defining a master
catalog.
For a user catalog, you may use any programmer logical unit, and any
ddname:
access 199 e
listds e (free
dlbl cat1 e dsn private cat1
amserv usercat
192