April 1, 1981
Comparison of CP andCMS Facilities for Debugging
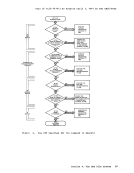
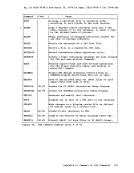
If vouCMS, you can choose the CP or :MS debuqqinq tools. Refer to Fiqure 18 for a comparison of the CP and :MS debugging tools.
r, FI} nction
,--------, settinq laddl"es::; ,stops. 1------ I D'lm')inq ,contents lof I printel". , I I I Displav in ql the COl- I tents ')f I stOl"aqe I and I cont rol , reqistel"s I at +-.he I I 1-------- IStol"ing- linf')r-m3. I t ion. I I I I I , , I I Tracin:l ti:>n. Can set only one address stop at a time. The dump is printed in hexadecimal format
withPOCDIC translation. The storage ad
dress of the first byte of each line is
identified at the left.
The display is typed in hexadecimal format
withEBCDIC translation. The CP command I 1isplays storage keys, floatinq-point regi-I sters and control registers. , The amount of information stored by the CP
command is limited only by the length of+-he input line. The information can be Fullword aligned when stored. CP stores data in floating-point and control reqis
ters, as well as in qeneral reqisters. CP
stores data in thepsw, but not in the CAW or CSW. However, data can be stored in the CAW by specifying the hardware ad dress in the STORE command. Cp t.races: • All interruptions, instructions, and
branches• SVC interruptions • I/O interruptions • Proqram interruptions • External interruptions • Pr-ivileged instructions • I/O operations • Virtual and real CCW's • All instructions
The CP trace is interactive.You can stop
it and display other fields.I I , , I L ________________ _
,CMS I I :an set up to 16 stopSI at a time. t I , The dump is printed in I decimal format. The I address of the first byte of , each line is identified
left. The contents of general, and floating-point reqisters I are printed at the beginninq , of the dump. , t
The display istyped in nex3.- I decimal format. The CMS I mands £g stoI:"3.qe , keys, floating-point reqistersl or control registers as the CPt command does. I I , , ------t
The:MS command stores up to , 12 bytes of information. :MS , stores data in the , registers but not in the , floating-point or control req-I isters. CMS stores data in the, PSW, CAW, and CSW. I :MS traces all SVC interrup
tions.CMS displays the
contents of general and
floating-point reqisters
before and aftera routine is
called. The parameter list is
recordedbefoI:"e a
routine is called., , , Fiqure 18. Comparison of CP and CMS Facilities for Debugging 222 eMS User's Guide
Comparison of CP and
If vou
r
,--------
with
dress of the first byte of each line is
identified at the left.
The display is typed in hexadecimal format
with
command is limited only by the length of
ters, as well as in qeneral reqisters. CP
stores data in the
branches
The CP trace is interactive.
it and display other fields.
,
left. The contents of general
The display is
The
tions.
contents of general and
floating-point reqisters
before and after
called. The parameter list is
recorded
routine is called.