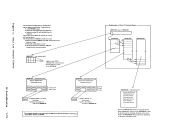
virtual machines. In so doing, the virtual machine with a higher
priority is considered for dispatching before a virtual
lower priority.
SET
where userid is the user's identification and nn is an integer value
in relation to other users in the
one of the factors considered in
position in relation to other users in
users are assigned from the available list, which is replenished
Pages that are
or pageable. The reserved page function gives a particular virtual
locked; they can be swapped, but only for the specified virtual
select the best page for swapping. The
been reached. If an available reserved page
reserved user selection, it is used whether or not the
reached.
The
SET
are all reserved, the
function can be specified in only one virtual machine at anyone
area in real storage large enough to contain the entire virtual=real
its true real storage location; only its page zero is relocated. The
virtual
1-32