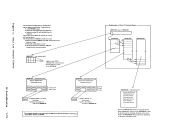
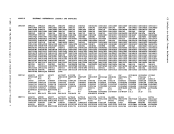
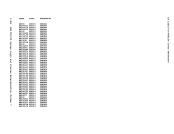
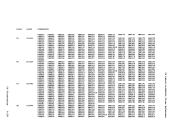
version of
The register specified as Rx contains the doubleword aligned virtual
storage address where the
stored. The Ry register contains the number of bytes to be stored
entered as an unsigned binary number.
If the
aachine. If it does support the
following data is returned to the virtual
specified by Rx):
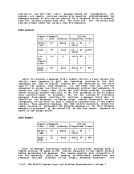
Address
version
byte is the level, and the third
byte is the
Change)
to determine the version
code.
the
Logout) area.
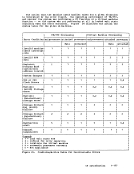
3 bytes, hexadecimal
1 byte, hexadecimal
2 bytes, hexadecimal
to
address.
The userid of the virtual
8 bytes, EBCDIC
8 bytes, hexadecimal
If
less, of extended identification data is appended to the first
described above.
issued the diagnose instruction.
that were stored.