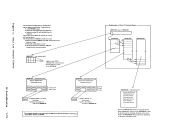
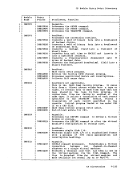
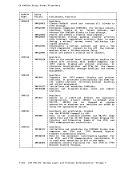
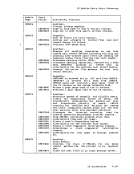
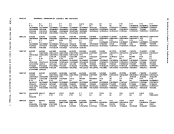
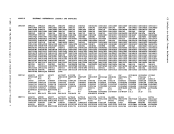
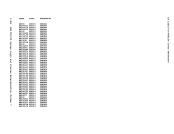
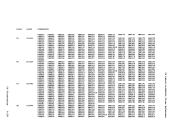
Action
Locks the virtual machine that was last dispatched.
Locks the virtual machine just built.
Locks the virtual machine being set as favored.
block.
Locks the virtual machine whose virtual device is being
reset when a real device is halted.
Locks each virtual
unlocked, or for whom accounting is being done.
Locks the virtual machine receiving transferred spool
files.
Locks the virtual machine of the dialed system, the virtual
virtual
being coupled.
Locks the virtual machine associated with a real device
block.
Locks the virtual
machine being autologged.
Locks the virtual machines receiving messages at
Locks each virtual machine active when the
Locks the virtual machine associated with a real device
block.
Locks the virtual machine associated with a queued
Locks the virtual machine
Locks the system operator.
Locks the virtual machine associated with a
NICBLOK.
Locks the virtual machine of the destination user for a
console task or the virtual machine associated with a
Locks the virtual
file or the virtual
Locks the virtual machine to which the channel is being
attached, or the the virtual machine from which the
channel is being detached.
Locks the virtual
detaching a real device.
Locks the virtual machine involved in detaching a real
device.
Locks the virtual machine to which the caller is
odules that
CP Introduction 1-175