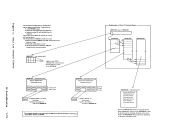
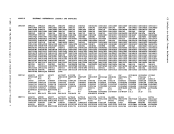
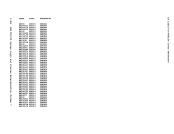
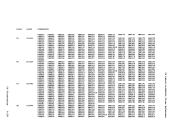
If DKKIOS receives an unsolicited interrupt or an I/O error for
scheduledI/O, a call is made to DKKFREE for either an IOBLOK, CPEXBLOK, or an IOERBLOK. DKKFREE will ensure that control is returned to the
processor that initiated the request.Shared Segment The shared seqment suufunction of VK/370 (DftKITS, DftKCFG, DftKCFB, DKKPGS, and DKKVKl) runs under the global system lock on either the main processor or the attached processor. All protected shared segments are
duplicated in a system that is generated for attached processor mode and
that is initialized on a machine with the multiprocessing feature.DKKCFG obtains sufficient storage to construct the duplicate page and
swap tables in contiguous storage. TheSHRTIBLE SHRPIGE pointer points
to the page and swap tables for themain processor, and the page and
swap tables for the attached processor are at a fixed displacement from
the page and swap tables for the main processor.DftKCFG initializes
both sets of page and swap tables. Initially, the two swap tables point
to theDlSD locations specified in DKKSBT. However, as the pages are
read into storage and then stolen, each shared page is allocated itsown DlSD slot and is pointed to by only one swap table entry.
The last user to purge a sharedsystem causes both sets of page and
swap tables to be released.One shared page table is reserved for use by each processor. This
includes both problem state and supervisor state execution on behalf of
a virtual machine. Toaccomplish this, each time a virtual machine running a shared system is locked, a test is made to determine whether
or not the virtual machine was last serviced on this processor. If it
was last serviced on the other processor, all of its shared page table
pointers in itssegment tables are switched to this processor's shared
pages.
DKKPTR is able to steal a shared pagefrom a shared page table
reserved for the processor it is running on without notifying the other
processor. The virtual page could not appear in the look-aside buffer
of the other processor.
The dispatcher releases theVKBLOK lock on LlSTUSER following the
check for pending interrupts (assuming no fast redispatch possible)
unless the virtualmachine was running one or more shared systems. In
the latter case theVKBLOK lock is not released until the DftKVKl scan
for a changed page is completed.DKKVKA scans all protected shared segments that the virtual machine used. For every changed page that it finds, DftKVKl checks whether or
not thesystem lock is held. If the system lock is held, the changed
page is returned to CP free storage. If thesystem lock is not held, DKKVKl marks the page table entry as invalid, marks the swap table entry
as in transit, and indicates that the core table entry is on the free
and flush lists. The other virtual machines can continue to use the
shared segments. The changed pages are replaced when thenext reference
to the changed page is made.
If the shared segment is violated, an errormessage (DKKVft1456) is
sent to the violator, and he is placed in console functionmode. The user may examine his PSW and registers to determine what caused the
viOlation. The user enters the BEGIN command toresume execution at the
point of interruption.1-180 IBM VK/370 System Logic and Problem Deter.ination--Voluae 1
scheduled
processor that initiated the request.
duplicated in a system that is generated for attached processor mode and
that is initialized on a machine with the multiprocessing feature.
swap tables in contiguous storage. The
to the page and swap tables for the
swap tables for the attached processor are at a fixed displacement from
the page and swap tables for the main processor.
both sets of page and swap tables. Initially, the two swap tables point
to the
read into storage and then stolen, each shared page is allocated its
The last user to purge a shared
swap tables to be released.
includes both problem state and supervisor state execution on behalf of
a virtual machine. To
or not the virtual machine was last serviced on this processor. If it
was last serviced on the other processor, all of its shared page table
pointers in its
pages.
DKKPTR is able to steal a shared page
reserved for the processor it is running on without notifying the other
processor. The virtual page could not appear in the look-aside buffer
of the other processor.
The dispatcher releases the
check for pending interrupts (assuming no fast redispatch possible)
unless the virtual
the latter case the
for a changed page is completed.
not the
page is returned to CP free storage. If the
as in transit, and indicates that the core table entry is on the free
and flush lists. The other virtual machines can continue to use the
shared segments. The changed pages are replaced when the
to the changed page is made.
If the shared segment is violated, an error
sent to the violator, and he is placed in console function
viOlation. The user enters the BEGIN command to
point of interruption.