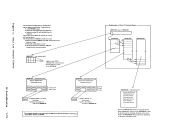
This option specifies that the selected virtual machine, in addition to remaining in queue, is guaranteed a specified minimum percentage of the
total processortime if it can use it. The favored execution option can
only be invoked by asystem operator with command privilege class A. The format of the command is as follows: r , SET FAVORED userid Inn I L ~ ~h~£~: userid identifies the virtual machine to receive favored execution
status.
nn is any valuefrom 1 through 99 and specifies the percentage
of the in-aueuetime slice that is guaranteed to this virtual machine. OFF specifies that the virtual machine is to be removed from favored execution status.
The percentage option of theSET FAVORED command is administered as
follows:
1. The in-queuetime slice is multiplied by the specified percentage
to arrive at the virtual machine's guaranteed processortime. 2. The favored virtual machine, when it is executable, is always
placed at the top of the dispatchable list until it has obtained
its guaranteed processortime. 3. If the virtual machine obtains its guaranteed processor time before
the end of its in-queue time slice, it is placed in the
dispatchable list according to its calculated dispatching priority.
4. In either case (2 or 3), at the end of the in-queuetime slice the
guarantee is recomputed as in step 1 and the process is repeated.Whether or not a percentage is specified, a virtual aachine with the favored execution option active is kept in the dispatching queues except
under the following conditions:• Entering CP console function mode • Loading a disabled PSW • Loading an enabled PSW with no active I/O in process • Logging on or off When the virtual machine becomes executable again, it is put back on the
executable list in Q1. If droppedfrom Q1, the virtual machine is
placed directly in Q2 and remains there even though itmay exhaust its
allottedamount of processor usage. Virtual machines with this option
are thus considered for dispatching more frequently than other virtualmachines. Note, however, that these options can impact the response time of
interactive users and that only one favored percentage user is allowed
at any giventime. CP Introduction 1-31
total processor
only be invoked by a
status.
nn is any value
of the in-aueue
The percentage option of the
follows:
1. The in-queue
to arrive at the virtual machine's guaranteed processor
placed at the top of the dispatchable list until it has obtained
its guaranteed processor
the end of its in-queue time slice, it is placed in the
dispatchable list according to its calculated dispatching priority.
4. In either case (2 or 3), at the end of the in-queue
guarantee is recomputed as in step 1 and the process is repeated.
under the following conditions:
executable list in Q1. If dropped
placed directly in Q2 and remains there even though it
allotted
are thus considered for dispatching more frequently than other virtual
interactive users and that only one favored percentage user is allowed
at any given