operation for a virtual machine means that the program of that virtual machine will be executed on the selected or named processor. It does
notimply that supervisory functions and the CP housekeeping functions
associated with that virtual machine will be handledby the same
processor.
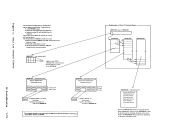
In attached processor systems, all realI/O operations and associated
interrupts are handledby the main processor. Virtual I/O initiated on
the attached processor that ismapped to real devices must transfer
control to themain processor for real I/O execution. Therefore,
benefitsmay be realized in a virtual machine "mix" by relegating those
virtual machines that have a high I/O-to-compute ratio to themain processor, and those virtual machines that have a high compute-to-I/O
ratio tothe attached processor. Such decisions should be carefully
weighed as every virtualmachine is in contention with other virtual aachines for resources of the system. A more important use of the affinity setting would be in applications
where there are virtual machineprogram requirements for special
hardware features that are available on one processor and not the other.Such features could be a performance enhancement such as virtual machine
assist (described later in the text) or a specialRPQ that is a requirement for a particular program's execution. VIRTUAL MACHINE ASSIST FEATURE The virtual machine assist feature is a processor hardware feature. It
i.proves the performance ofVM/370. Virtual storage operating systems,
which run inproblem state under the control of V8/370, use aany privileged instructions and SVCs that cause interrupts that V8/370 must handlee ihen the virtual machine assist feature is used, many of these
interrupts are intercepted and handled by the processor; and,
consequently,V!/370 performance is improved. See V!/~70 ~!anninq ~ng ~ystem ~en~~§!ion ~uidg for a list of the processors on which virtual machine assist is available. The virtual machine assist feature intercepts and handles
interruptions caused bySVCs (other than SVC 76), invalid page
conditions, and several privileged instructions. AnSVC 76 is never
handled by the assist feature; it is always handledby CP. The
processing of the following privileged instructions is handled by this
feature:
LRASTCTL RRB ISK SSK IPK STNS! STOS! SSK LPSi SPKA (load real address)
(store control)
(reset reference bit)
(insert storage key)
(set storage key)
(insertPSi key)
(store thenAND system mask) (store then OR system mask)
(setsystem mask) (load PSi) (set PSi key from address)
Although the assist feature was designed toimprove the performance of YK/370, virtual aachines may see a performance improvement because more resources are available for virtual.machine users. CP Introduction 1-35
not
associated with that virtual machine will be handled
processor.
In attached processor systems, all real
interrupts are handled
the attached processor that is
control to the
benefits
virtual machines that have a high I/O-to-compute ratio to the
ratio to
weighed as every virtual
where there are virtual machine
hardware features that are available on one processor and not the other.
assist (described later in the text) or a special
i.proves the performance of
which run in
interrupts are intercepted and handled by the processor; and,
consequently,
interruptions caused by
conditions, and several privileged instructions. An
handled by the assist feature; it is always handled
processing of the following privileged instructions is handled by this
feature:
LRA
(store control)
(reset reference bit)
(insert storage key)
(set storage key)
(insert
(store then
(set
Although the assist feature was designed to