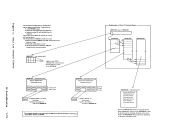
External Interruption TIBER IRTERRUPTION If DBKPSAEI is entered because of a tiaer interruption, the state of the
aachineaust be deterained. If the aachine was in wait state, control
is transferred toDBKDSPCH, and the aachine stays idle until another
interruption occurs. If the machine is in probleastate
l the address of
the current user'sVBBLOK is obtained froa RURUSER. The user's current PSW (VBPSW) is updated fro. the external interruption old PSW, the
address of the currentVBBLOK is placed in register 11, and control is
transferred toDBKDSPCH. Por additional information about tiaers, see "Virtual Tiaer Baintenance." EXTERRAL INTERRUPTION If D!KPS!EX ~~ cntersd because the vpe~atOL pLesseu ~ne console
interrupt button(IRTERRUPT), a CPEXBLOK is stacked to do the following: • Reference the current systea operator's VBBLOK (DBKSYSOP). • Disconnect this virtual machine. The operator can now log on froa another terainal. Pressing the
console interrupt button activates an alternate operator's console.
Rote: If this interruptCOaes froa the attached processor, it is
ignored.Por a description of the processing of the external interruption coaaand, refer to .odule DBKCPB in Section 2. See nBultiprocessor External Interrupts" for a discussion of external
interrupts that occur in attached processoraode. EXTEBDED VIRTUAL EXTERNAL INTERRUPTIONS To reflect external interruptions to a virtual aachine, DBKDSPE queues
anXINTBLOK on a chain pointed to by VBPXIBT in the VBBLOK. The XIITBLOKs are chained sequentially by the XIRTSORT field that contains
the collatingnuaber of the pending interruption. If aore than one
interruption has thesaae collating nu.ber, the interruption codes are ORed together in the XIRTCODE field for possible siaultaneous
reflection.When a virtual machine is enabled for external interruptions. the XIBTBLOK queue for that machine is searched for an eligible block. In XIBTBLOK is eligible for reflection if one or aore bits of the XIBTBISK field match the bits in the rightmost halfword of control register O. If the interruption was an interruption such as CPU timer or clock
coaparator, the block is left chained because reflection does not reset
these interruptions. If the reflected interruption(s) does not
represent all those coded in theXIRTBASK field, the block is left
chained and only the interruptions that were reflected are reset. In
all other conditions, theXINTBLOK is unchained and returned to free
storage.
1-76IBB V8/370 Systea Logic and Proble. Deteraination--Voluae 1
aachine
is transferred to
interruption occurs. If the machine is in problea
l
the current user's
address of the current
transferred to
interrupt button
console interrupt button activates an alternate operator's console.
Rote: If this interrupt
ignored.
interrupts that occur in attached processor
an
the collating
interruption has the
reflection.
coaparator, the block is left chained because reflection does not reset
these interruptions. If the reflected interruption(s) does not
represent all those coded in the
chained and only the interruptions that were reflected are reset. In
all other conditions, the
storage.
1-76