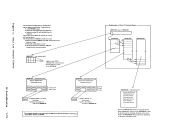
and the model-dependent data is stored in the extended logout area. The
machine check handler uses these fields to analyze the error, format an
error record, and write the record out on the error recording cylinder
ofSYSRES. If the machine fails to recover from the malfunction through its own recovery facilities, the machine check handler is notified by a machine
check interruption. An interruption code, noting that the recovery
atteaptwas unsuccessful, is inserted in the fixed logout area. The machine check handler then analyzes the data and attempts to keep the system as fully operational as possible.
Recovery from machine malfunctions can be divided into the following
categories: functional recovery, system recovery, operator-initiatedrestart, and system repair. These levels of error recovery are discussed
in their order of acceptability, functional recovery being most
acceptable and system repair being least acceptable:X~NCTIQNAL Rl£OVERY: Functional recovery is recovery from a machine
check without adverse effect on thesystem or the interrupted user.
This type of recovery can be madeby processor retry, the ECC facility,
or the machine check handler. Processor retry and ECC error correcting
facilities are discussed separately in this section because they are
significant in the total error recovery scheme. Functional recovery byMCH is made by correcting storage protect feature (SPF) keys and
intermittent errors in real storage.~IST~~ RECO!~!!: System recovery is attempted when functional recovery
is impossible.System recovery is the continuation of systea operations
at the expense of the interrupted user, whose virtual machine operation
is terminated.System recovery can only take place if the user in
question is not critical to continued systea operation.An error in a system routine that is considered to be critical to system operation
precludes functional recovery and would require logout and a systemdump followed by reloading the system. OPERATOR-IN!I!ATE~ !t~ST!!I: When ,the errors may have caused a loss of
supervisor or system integrity, the system is put into a disabled wait
state. The operator is instructed to run the standalone error recovery
(SEREP) program and thenIRa nua11y restart the system. SYSTE~ REP!!R: System repair is recovery that requires the services of
aaintenance personnel and tak'es place at the discretion of the opera tor.Usually, the operator has tried to recover by system-supported restart
one ormore times with no success. SYSTEM/370 RECOVERY FEATURES The operation of the Machine Check Handler depends on certain automatic
recovery actions taken by the hardware and on logout information given
to itby the hardware.
Processor errors are autoaatica11y retried by microprogram routines.
These routines save source data before it is altered by the operation.When the error is detected, a aicroprograa returns the processor to the
beginning of the operation, or to a pointwhere the operation was executing correctly, and the operation is repeated. After several
unsuccessful retries, the error is considered peraanent.
CP Introduction 1-151
machine check handler uses these fields to analyze the error, format an
error record, and write the record out on the error recording cylinder
of
check interruption. An interruption code, noting that the recovery
atteapt
Recovery from machine malfunctions can be divided into the following
categories: functional recovery, system recovery, operator-initiated
in their order of acceptability, functional recovery being most
acceptable and system repair being least acceptable:
check without adverse effect on the
This type of recovery can be made
or the machine check handler. Processor retry and ECC error correcting
facilities are discussed separately in this section because they are
significant in the total error recovery scheme. Functional recovery by
intermittent errors in real storage.
is impossible.
at the expense of the interrupted user, whose virtual machine operation
is terminated.
question is not critical to continued systea operation.
precludes functional recovery and would require logout and a system
supervisor or system integrity, the system is put into a disabled wait
state. The operator is instructed to run the standalone error recovery
(SEREP) program and then
aaintenance personnel and tak'es place at the discretion of the opera tor.
one or
recovery actions taken by the hardware and on logout information given
to it
Processor errors are autoaatica11y retried by microprogram routines.
These routines save source data before it is altered by the operation.
beginning of the operation, or to a point
unsuccessful retries, the error is considered peraanent.
CP Introduction 1-151