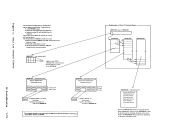
The initial analysis subroutine of DMKMCH receives control by a machine check interruption. To minimize the possibility of losing logout
information by recursive machine check interruptions, the machine check
newPSi gives control to DMKMCH with the system disabled for further
interruptions. There is always a danger that amachine malfunction may occur immediately after DMKMCH is entered and the system is disabled for
interruption. Disabling all interruptions is only a temporarymeasure to give the initial analysis subroutine time to make the following emergency provisions: • It disables for soft machine check interruptions. Soft recording is
not enabled until the error is recorded.• It saves the contents of the fixed and extended logout areas in the machine check record. • It alters the machine check new PSi to point to the term subroutine.
The term subroutine handles second machine check errors.• It enables the machine for hard machine check interruption. • If a virtual user was running when the interruption occurred, the
running status (GPRs, FPRs,PSi, M.C. old PSi, CRs, etc.) is saved in
the user'sVMBLOK. • It initially examines the machine check data for the following error
types:MCIC=ZERO PSi invalid System damage Timing facilities damage Channel inoperative on 3031/3032/3033 processor
The occurrence of any of these errors is considered uncorrectable byDMKMCH; the primary system operator is informed, the error is
formatted and recorded, and the system enters a wait state, code001 or 013~ • If the instruction processing damage bit is on, it tests for the following types of aalfunctions: Multiple-Bit Error in Main Storage --Control is given to the main storage analysis subroutine. SPF Key Error --Control is given to the SPF analysis subroutine.
Retry failed --If the processor was in supervisor state the error
is considered uncorrectable and theVM/370 system is terminated.
If the processor was in problea state, the virtual machine is
reset or terainated and thesystem continues operation. • If processor retry or ECC was successful on a soft error, control is
given to the soft recording subroutine toformat the record, write it
out on the error recording cylinder, and update the count of soft
error occurrences.• If external damage was reported,
recording subroutine to foraat the
error recording cylinder.
control is
record and
given to the soft
write it out on the
CP Introduction 1-153
information by recursive machine check interruptions, the machine check
new
interruptions. There is always a danger that a
interruption. Disabling all interruptions is only a temporary
not enabled until the error is recorded.
The term subroutine handles second machine check errors.
running status (GPRs, FPRs,
the user's
types:
The occurrence of any of these errors is considered uncorrectable by
formatted and recorded, and the system enters a wait state, code
Retry failed --If the processor was in supervisor state the error
is considered uncorrectable and the
If the processor was in problea state, the virtual machine is
reset or terainated and the
given to the soft recording subroutine to
out on the error recording cylinder, and update the count of soft
error occurrences.
recording subroutine to foraat the
error recording cylinder.
control is
record and
given to the soft
write it out on the
CP Introduction 1-153