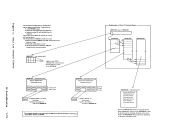
If the CP termination flag is not set, a check is made to determine
if an IOERBLOKwas built by the channel control subroutine.
If anIOERBLOK was not built, DMKIOECC is called to record the
channel check record on the error recording cylinder. Thesystem operator is then sent a message (DMKCCH6011 or DeKCCH602I) informing hi. of the error and control is then returned to DMKIOS to continue system operation.
If anIOERBLOK was built, control is returned to DMKIOS, which calls
the appropriateERP. Whether or not recovery is successful, DMKIOS eventually calls DMKIOE to record the channel check record. DMKIOE examines the status of the in CSW error in the IOERBLOK to determine if
itwas a channel error; if so, it finds the length and pointer to the
channelcheck record and records the error on the error recording
cylinder. If thiswas not a channel error, DMKIOE continues normal
processing.INDIVIDUAL ROUTINES A separate channel error analysis routine is provided for each type of
channel for whichDMKCCH can be used. The purpose of these routines and
the channel control subroutine is to analyze the channel logout to
determine the extent of damage and to create a sequence and termination
code to be placed in theECSW in the IOERBLOK. At system
initialization, the correct model dependent channel recovery routine is
loaded and the storage necessary to support the routine is allocated.
The model-dependent error analysis subroutines and routines and their
functions are as follows:
Since all
subroutine
subroutine:
of
is
these systems
used to handle
have
all
integrated channels one
of these processor types.
common
This• Indicates CP termination if the ECSW is not complete, the channel has
been reset, the reset codes are invalid, or theI/O interface is
inoperative.• Moves the ECSW to the IOERBLOK • Moves the hardware stored unit address and the I/O extended logout to
the channel check record• Sets the I/O extended logout area and ECSi area to ones • Returns control to the channel control subroutine
The2860 logout area is checked to determine if a complete logout
exists; if not,CP termination is necessary. CP Introduction 1-159
if an IOERBLOK
If an
channel check record on the error recording cylinder. The
If an
the appropriate
it
channel
cylinder. If this
processing.
channel for which
the channel control subroutine is to analyze the channel logout to
determine the extent of damage and to create a sequence and termination
code to be placed in the
initialization, the correct model dependent channel recovery routine is
loaded and the storage necessary to support the routine is allocated.
The model-dependent error analysis subroutines and routines and their
functions are as follows:
Since all
subroutine
subroutine:
of
is
these systems
used to handle
have
all
integrated channels one
of these processor types.
common
This
been reset, the reset codes are invalid, or the
inoperative.
the channel check record
The
exists; if not,