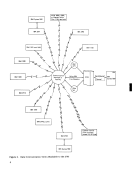
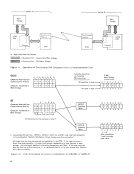
via Data
Adapters
r-----,
Base
via Data
Controls and
Storage
Adapters
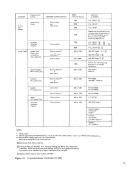
#4-Lines per Line Set-Max. of 8***per sis line set.
Max. of 4 per Sync. line set.
Legend:
S/S-Start/Stop type operations
Sync. -Synchronous type operations
*-Check Figure 8 for various line base configurations.
**-These maximums are influenced by the Feature linitations Per
in the
***-Except where this is increased to 16 lines by an expander feature.
Refer to the 2712 Modell and Model 2 Adapter Features for details of how the 2712
expander features increase the number of available lines.
Figure 3. 2703-Internal
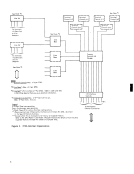
To Multiplexer
Channel Connection