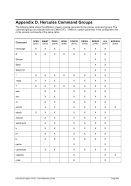
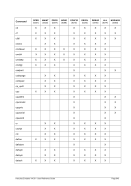
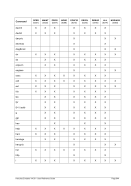
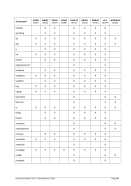
5.44 LPARNUM (LPAR
identification number)
5.44.1 Function
The LPARNUM system parameter sets the LPAR identification number. It specifies the one- or two-digit
hexadecimal LPAR identification number stored by the STIDP instruction, or BASIC. If a one-digit number
from 1 to F (hexadecimal) is specified, then STIDP stores a format-0 CPU ID, unless a subsequent
“CPUIDFMT 1” statement is specified. If zero or a two-digit hexadecimal number, except 10 (hexadeci-
mal), is specified, then STIDP stores a format-1 CPU ID. For LPARNUM 10 the current CPUIDFMT is not
changed. If LPARNUM is BASIC, then the STIDP instruction stores a basic-mode CPU ID. The default is
LPARNUM 1 with a format-0 CPU ID.
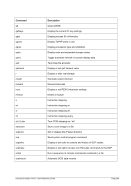
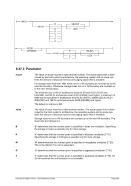
5.44.2 Syntax
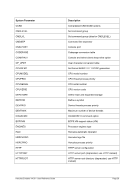
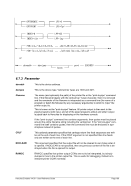
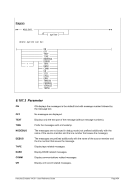
Descriptive
1 n nn
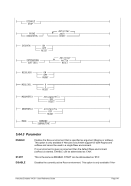
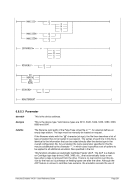
Diagram
¬¬¬§¬¬¬ ¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬ÊÍ
¬¬ ¬¬ 1 ¬¬¬¬¬«
1...F ¬¬¬«
¬¬¬¬¬«
¬¬ ¬ nn ¬¬¬
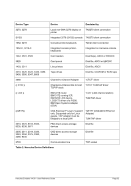
5.44.3 Parameter
BASIC
Specifies that STIDP stores a basic-mode CPU ID.
1
Specifies the one-digit hexadecimal LPAR identification number. The STIDP in-
struction stores a format-0 CPU ID. This is the default.
1 … F
Specifies the one-digit hexadecimal LPAR identification number. The STIDP in-
struction stores a format-0 CPU ID, unless a subsequent “CPUIDFMT 1” statement
is specified.
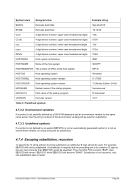
0
Specifies 0 as LPAR identification number. The STIDP instruction stores a format-1
CPU I
D.
nn
Specifies the two-digit hexadecimal LPAR identification number (except 10 hexa-
decimal). For LPARNUM 10 the current CPUIDFMT is not changed. The STIDP in-
struction stores a format-1 CPU I
D.