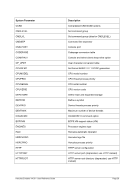
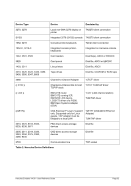
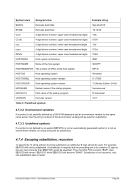
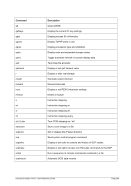
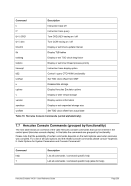
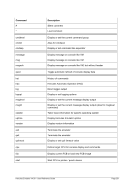
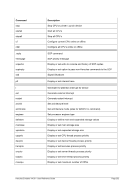
8.96 MAINSIZE (Display or set main storage size)
8.96.1 Function
The MAINSIZE command is used to specify the size of the main storage. Given without an argument the
MAINSIZE command displays the current size of the main storage. Storage is allocated in megabytes,
unless a specific unit is specified. The actual upper limit of the main storage is determined by the host
system's architecture, operating system, and on some systems the amount of physical memory and
paging space you have available. The practical limit depends on the maximum amount of storage that
can be obtained by “malloc” (usually around 1 GB on 32-bit platforms; on 64-bit platforms the value
should only be limited by available paging space).
When increasing the main size Hercules attempts to allocate first the new storage. If the new allocation is
successful then the previously allocated memory will be freed. This is to prevent a situation where the old
memory is freed first, then the new allocation fails and a reallocation of the memory in the previous size
also fails because of storage fragmentation and therefore leaving Hercules without memory.
When decreasing the main storage the memory will stay allocated in the previous size but the storage
size will appear as decreased. Subsequent increases will not reallocate memory unless they go over the
already allocated amount.
An additional optional argument determines the locking state of the allocated memory (page lock by host
operating system). The LOCKED option indicates that the memory is to be locked into storage while UN-
LOCKED (
the default) indicates that the memory is not locked into the storage.
Please note that Hercules preserves the last locking state of MAINSIZE. Once storage is locked, any sub-
sequent change to the main storage size will honor the existing lock state of memory unless the lock state
is specified again on the MAINSIZE command.
Caution: Do not lock main storage unless sufficient real memory is available to back up the request.
Failure to do so may require the host system to be rebooted.
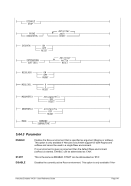
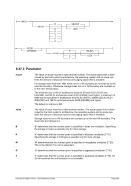
8.96.2 Syntax
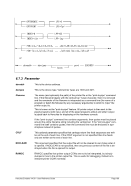
Descriptive
msize[ ]
]
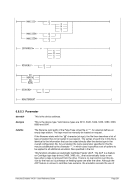
Diagram
Êʬ¬¬ ¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬ÊÍ
~¬¬¬ ¬¬¬® ¬®
msize ¬¬¬¦¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¦¬¬
¬¬¬ ¬¬¬«
P ¬¬¬«
¬¬¬ ¬¬¬