5.82 Process and Thread Priorities
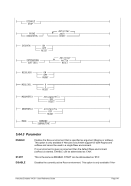
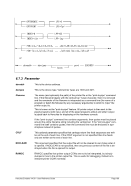
This section covers details regarding the priority settings within Hercules. The relevant system parame-
ters are:
5.82.1 Process Priorities
Under Linux a process is a thread and thread priority information applies instead.
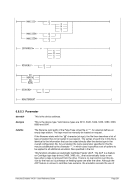
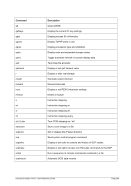
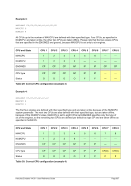
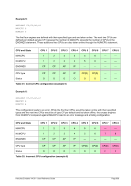
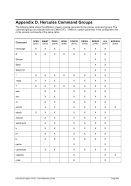
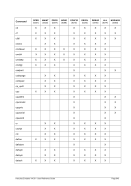
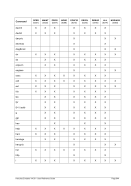
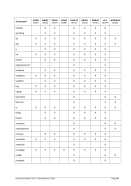
For Windows the following conversions are used for translating Unix process priorities to Windows priority
classes:
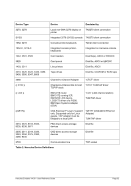
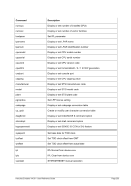
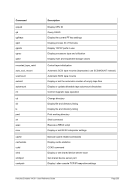
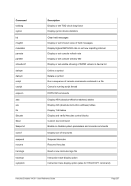
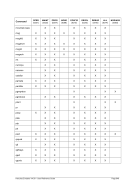
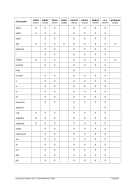
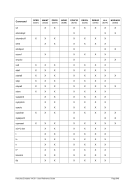
Unix
Process Priority
Windows
Priority Class
Meaning
-20 to -16
Realtime
Process that has the highest possible priority. The threads of
the process preempt the threads of all other processes, inclu-
ding operating system processes performing important tasks.
For example, a real-time process that executes for more than a
very brief interval can cause disk caches not to flush or cause
the mouse to be unresponsive.
-15 to -9
High
Process that performs time-critical tasks that must be executed
immediately. The threads of the process preempt the threads of
normal or idle priority class processes. An example is the Task
List, which must respond quickly when called by the user, re-
gardless of the load on the operating system. Use extreme care
when using the high-priority class, because a high-priority class
application can use nearly all available CPU time.
-8 to -1
Above Normal
Process that has priority above the Normal class but below the
High class.
0 to 7
Normal
Process with no special scheduling needs.
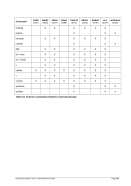
8 to 15
Below Normal
Process that has priority above the Idle class but below the
Normal class.
16 to 20
Low
Process whose threads run only when the system is idle. The
threads of the process are preempted by the threads of any
process running in a higher priority class. An example is a
screen saver. The idle-priority class is inherited by child pro-
cesses.
Table 8: Process Priority Conversions