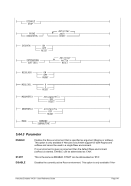
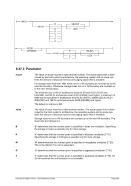
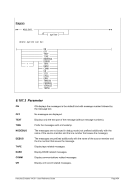
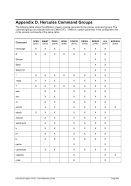
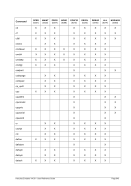
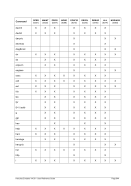
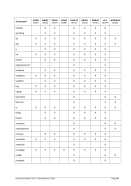
Diagram
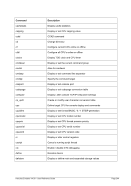
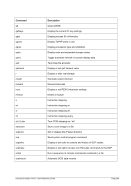
Êʬ¬¬ ¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬Ê
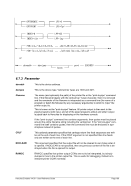
-n ¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬ name
--
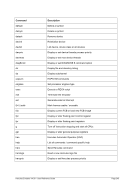
ʬ¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬Ê
-s ¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬ mask
--netmask
ʬ¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬Ê
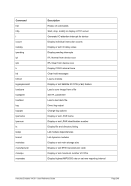
-m ¬
¬¬¬§¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬ mac ¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬«
--
ʬ¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬Ê
-t ¬
¬¬¬§¬¬¬ mtu
--
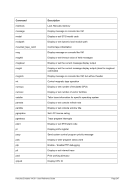
ʬ¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬Ê
-i ¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬§¬¬¬ ibuff ¬¬¬«
--
ʬ¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬Ê
-k ¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬§¬¬¬ kbuff ¬¬¬«
--
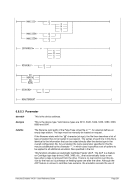
ʬ¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬ guestip ¬¬¬ hostip ¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬ÊÍ
-d ¬¬¬¬¬¬«
--debug
6.9.2.3 Parameter
devaddr
This is the device address.
CTCI
This specifies the CTCI device/protocol type.
-n name
For Linux: Specifies the name of the tunnel device to use. The default name is
“/dev/net/tun”, which is correct for version 2.4 and above of the Linux kernel.
For Windows: Identifies the host network adapter. If your network adapter does
not have a permanent (static) IP address assigned to it (e.g. you use DHCP and
have a dynamic IP assigned) then instead of specifying an IP address as the
second parameter in the device statement, you must specify the MAC address of
the adapter. In this case the second argument (hostip) must be coded as “0.0.0.0”.
This is simply a placeholder because two IP addresses are expected to satisfy the
device definition syntax.
--dev name
This is the same as “-n name”.
-s mask
This is the netmask to be configured on the link. Note: Since this is a point-to-point
link netmask is meaningless from the perspective of the actual network device.
--netmask mask
This is the same as “-s mask”.