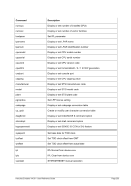
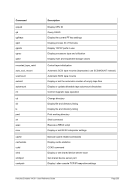
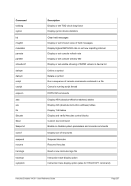
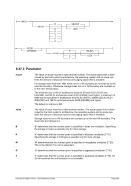
6.9.7 PTP (MPCPTP/PCPTP6 Channel-to-Channel link)
6.9.7.1 Function
The PTP is a point-to-point link to the driving system’s TCP/IP stack. From the point of view of the guest
operating system in the Hercules machine it appears to be an MPCPTP and/or MPCPTP6 ESCON CTC
link to another guest operating system.
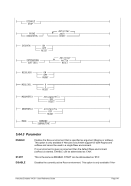
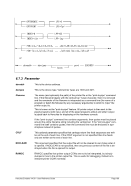
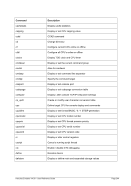
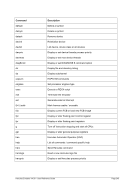
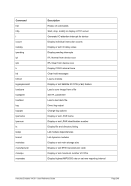
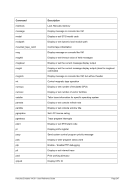
6.9.7.2 Syntax
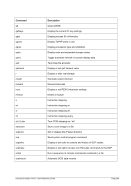
Descriptive
PTP -n --name]
---mac]
---mtu ]
*Linux only
[-i --ibuff
*Windows only
[-k --kbuff 4
*Windows only
---
---
[-d --debug]
guest1 host1
[guest2 host2]
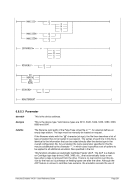
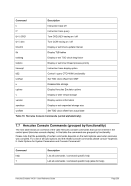
Diagram
Êʬ¬¬ ¬¬¬ PTP ¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬Ê
-n ¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬ name
--
ʬ¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬Ê
-m ¬
¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬ mac ¬¬
--
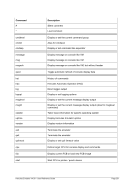
ʬ¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬Ê
-t ¬
¬¬¬§¬¬¬ mtu
--
ʬ¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬Ê
-i ¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬§¬¬¬ ibuff ¬¬¬«
--
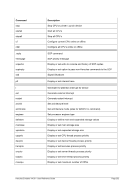
ʬ¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬Ê
-k ¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬§¬¬¬ kbuff ¬¬¬«
--