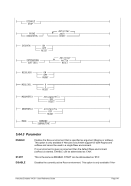
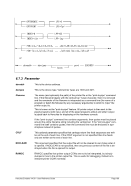
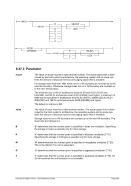
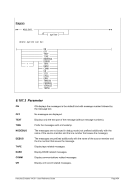
7.5.2 Syntax
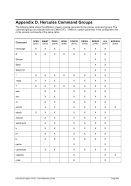
Descriptive
nn
command [&n &* &$ [...]]"
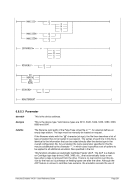
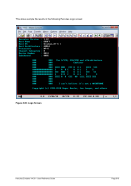
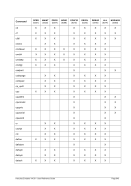
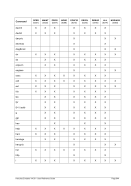
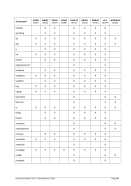
Diagram
nn ¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬Ê
¬¬¬
¬¬¬
command ¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬ " ¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬ÊÍ
¬¬¬ ¬¬¬¬«
~¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬®
¬¬¬
¬¬¬ ¬¬¬§¬ ¬¬ &n ¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬
¬¬¬ &* ¬¬¬«
&$ ¬¬¬
7.5.3 Parameter
PFnn This identifies the PF key to be defined, where nn is a number from 01 to 48. This
number must be specified with the leading zero for PF keys 1 - 9 (PF01, …, PF09).
SUBST This indicates that the PF key data might contain substitution placeholders (&n, see
below).
IMMED This indicates the point in time when the PF key is processed. IMMED indicates that the
PF data is processed when the PF key is pressed.
DELAY This indicates the point in time when the PF key is processed. DELAY indicates that the
PF data is displayed on the command line when the PF key is pressed. The data may
then be modified if necessary. To finally process the PF data the “ENTER” key must be
pressed.
HERC The command target for the assigned command is the Hercules Emulator.
SCP The command target for the assigned command is the System Control Program (the
guest operating system running under Hercules).
PSCP The assigned command is a System Control Program (guest operating system) priority
command.
command This defines the command that is to be assigned to the PF key.
&n A substitution placeholder is identified by an ampersand (“&”), followed by a decimal
number from 0 to 9. If two ampersands are detected (“&&”) then a single ampersand is
substituted.
&* Variable “&*” represents all of the remaining tokens beyond the last substitution variable
used. A single space is added between each token. Tokens can be enclosed in paired
single or double quotes. The quotes are included as part of the token string.
&$ Variable “&$” represents the data remaining on the line past token 9. Variable “$*” (see
below) does include the data from “&$”.A single space is added between each token.