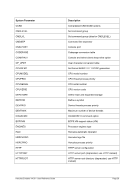
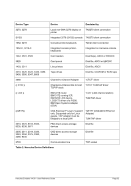
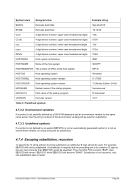
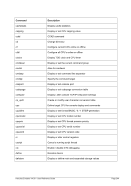
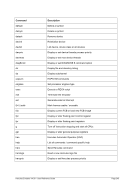
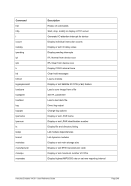
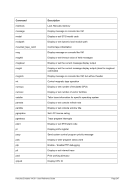
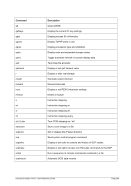
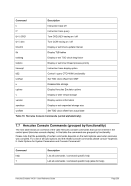
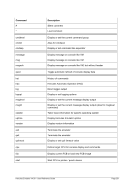
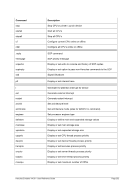
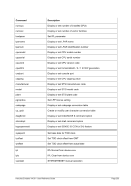
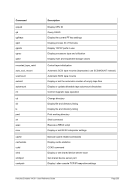
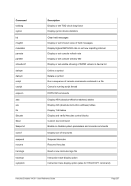
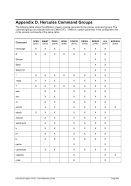
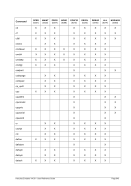
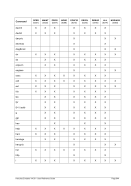
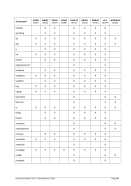
8.174.4 Examples
Example 1:
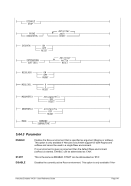
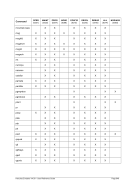
Specify year 1900 as the base date for the TOD clock and use an offset of 28 years.
HHC00013I Herc command: 'sysepoch 1900 +28'
Figure 309: SYSEPOCH command (with offset)
Example 2:
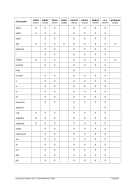
Specify year 1960 as the base date for the TOD clock without an offset.
HHC00013I Herc command: 'sysepoch 1960'
Figure 310: SYSEPOCH command (without offset)