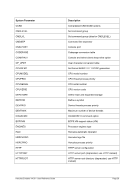
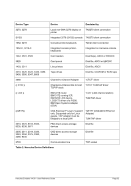
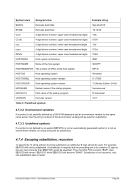
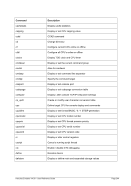
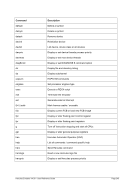
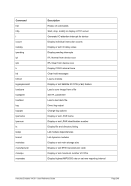
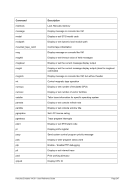
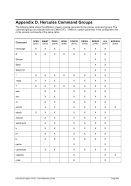
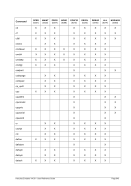
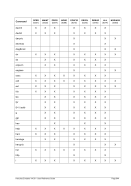
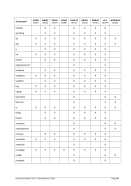
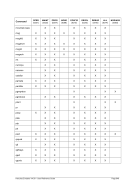
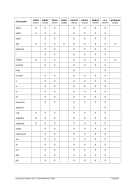
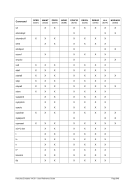
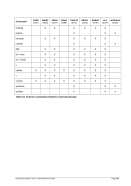
5.29.4 Examples
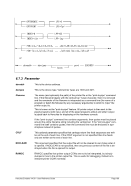
Example 1:
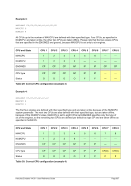
Specify 4 engines of type CP, 2 engines of type AP and 2 engines of type IP.
ENGINES CP,CP,CP,CP,AP,AP,IP,IP
or
ENGINES 4*CP,2*AP,2*IP
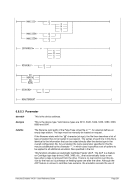
Example 2:
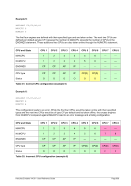
Specify 4 engines of type CP, 1 engine of type AP, 1 engine of type IP and 2 engines of type IL.
ENGINES CP,CP,CP,CP,AP,IP,IL,IL
or
ENGINES 4*CP,AP,IP,2*IL
Example 3:
Specify 3 engines of type CP and 1 engines of type IL.
ENGINES CP,CP,CP,IL
or
ENGINES 3*CP,IL