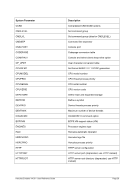
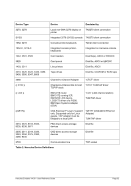
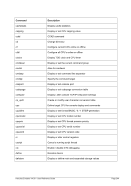
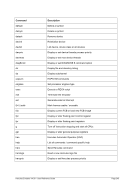
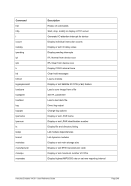
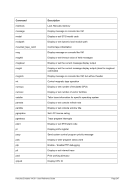
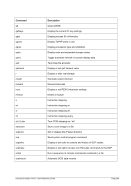
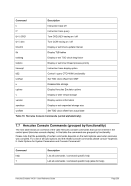
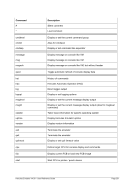
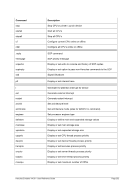
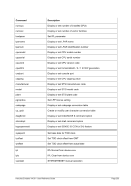
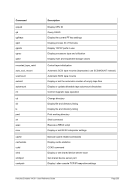
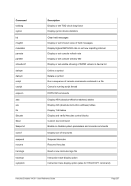
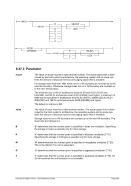
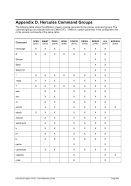
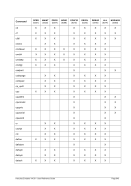
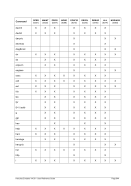
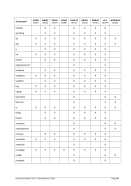
8.99.4 Examples
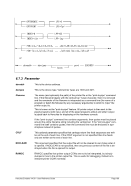
Example 1:
Change the MAXRATES interval from the default value (or the last manually set interval value) to 60
minutes.
HHC00013I Herc command: 'maxrates 60'
HHC02204I maxrates set to 60 minutes
Figure 187: MAXRATES command (set the interval time)
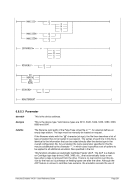
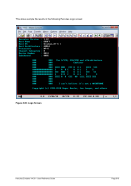
Example 2:
Display the maximum observed MIPS and I/O rates during the last interval.
HHC00013I Herc command: 'maxrates'
HHC02272I Highest observed MIPS and IO/s rates:
HHC02272I From Thu Apr 19 22:58:34 2012 to Fri Apr 20 22:58:34 2012
HHC02272I MIPS: 105.333858
HHC02272I IO/s: 3068
HHC02272I From Fri Apr 20 22:58:34 2012 to Fri Apr 20 23:06:38 2012
HHC02272I MIPS: 5.678100
HHC02272I IO/s: 54
HHC02272I Current interval is 1440 minutes
Figure 188: MAXRATES command (display maximum rates)