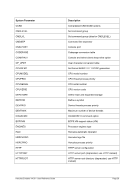
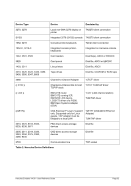
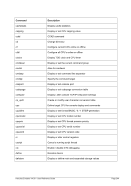
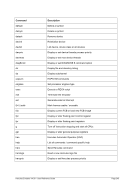
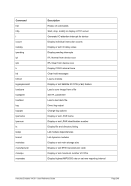
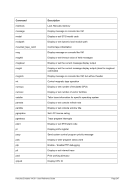
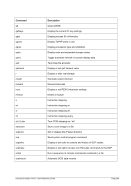
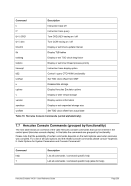
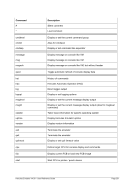
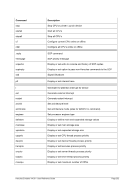
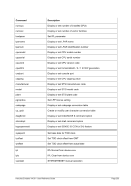
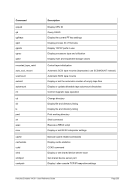
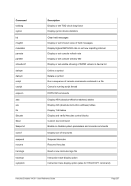
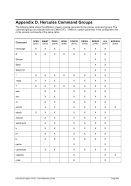
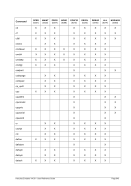
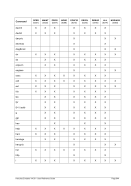
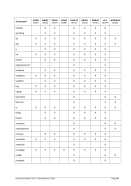
5.79 TZOFFSET (TOD c
lock offset from GMT)
5.79.1 Function
TZOFFSET is used to define the offset of the TOD clock from the current system time. For GMT use the
default value (0000). For time zones west of Greenwich specify a negative value (example: -0500 for US
Eastern Standard Time, -0800 for US Pacific Standard Time). For time zones east of Greenwich, specify
a positive value (example: +0100 for Central European Time, +0930 for South Australian Time).
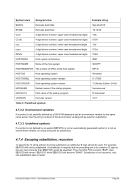
5.79.2 Syntax
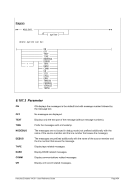
Descriptive
+hhmm -hhmm
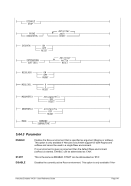
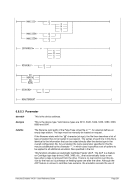
Diagram
¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬ÊÍ
+hhmm ¬¬¬«
-hhmm
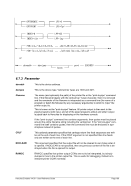
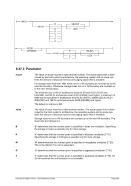
5.79.3 Parameter
0000
GMT time (0000 is the default value). Please note that this is also the correct set-
ting if your system time (the time of the operating system on which Hercules is run-
ning) is set to local time rather than GMT.
hhmm
Use a positive time in hours and minutes for time zones east of Greenwich.
hhmm
Use a negative time in hours and minutes for time zones west of Greenwich.
5.79.4 Examples
Example 1:
Set the offset of the TOD clock from the current system time to Central European Time.
TZOFFSET +0100