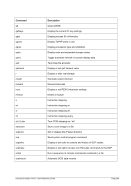
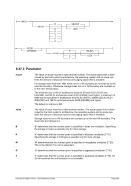
G
‘G’ determines that the number given is specified in gigabytes (multiplier 2**30).
T
‘T’ determines that the number given is specified in terabytes (multiplier 2**40). On
32-bit machines the unit terabytes is not available.
LOCK
Attempt to lock the storage (pages locked by the host operating system).
UNLOCK
Leave the store unlocked (no pages locked by the host operating system). This is
the default.
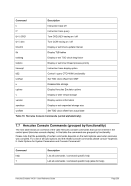
Notes:
The actual upper limit is determined by the host system’s architecture and operating system, the guest
operating system and the amount of physical memory and available paging space.
The total of MAINSIZE and XPNDSIZE on host systems with a 32-bit architecture will be limited to less
than 4G; host systems with a 64-bit architecture will be limited to less than 16E.
Use of storage sizes greater than supported by the guest operating system may generate incorrect
results or error conditions within the guest operating system.
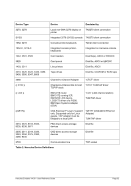
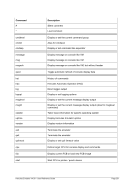
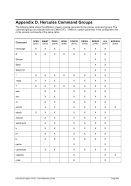
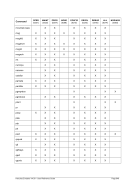
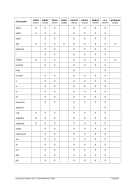
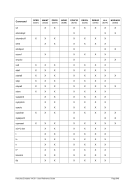
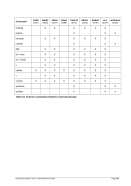
5.80.4 Overview Storage Allocation Units
Unit
Multiplier
Name (Symbol)
IEC Name (IEC Symbol)
Restrictions
M
2**20
Megabyte (MB)
Mebibyte (MiB)
G
2**30
Gigabyte (GB)
Gibibyte (GiB)
T
2**40
Terabyte (TB)
Tebibyte (TiB)
Not on 32-bit machines
Table 7: Storage Allocation Units
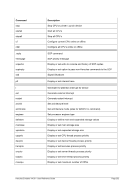
5.80.5 Examples
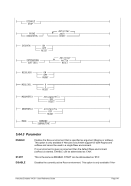
Example 1:
Set the size of the expanded storage to 256 MB. Do not lock the memory into the storage.
XPNDSIZE 256
or
XPNDSIZE 256M
or
XPNDSIZE 256 UNLOCK
or
XPNDSIZE 256M UNLOCK