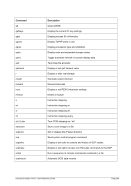
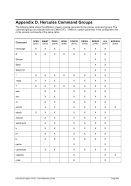
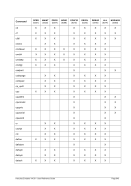
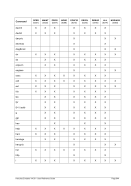
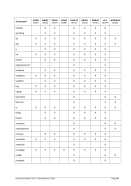
6.7 Line Printer Devices
6.7.1 Function
The line printer device statement defines a printer to the Hercules configuration. The argument specifies
the name of a file to which the printer output will be written. The output is written in the form of variable
length lines of ASCII characters, delimited by line feeds or carriage return line feed sequences. Trailing
blanks are removed from each line. Carriage control characters are translated to blank lines or ASCII
form feed characters. If the file exists it will be overwritten.
If the filename begins with the vertical bar '|' pipe character, then it is removed and the remainder of the
filename is interpreted as a command line (the name of a program or batch file followed by any necessary
arguments) to which to "pipe" the printer output to. This is known as the "print-to-pipe" feature. All printer
output is then sent to the piped programs stdin input, and all of the piped programs stdout and stderr out-
put is piped back to Hercules for displaying on the hardware console.
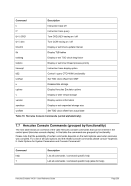
SOCKDEV indicates that the line printer is a socket device wherein the filename is actually a socket spe-
cification in the form host:port instead of a device filename. The device then accepts remote connections
on the given TCP/IP port and writes data to the socket instead to a device file. A Windows software that
supports a socket printer is Fish's "HercPrt" (Hercules Remote Printer Spooler). It spools the print output
from a Hercules socket printer and creates either PDF, RTF or just plain text files. A control file enables
HercPrt to split the printouts on job separator page boundaries and name the file according the actual job
accounting field values.
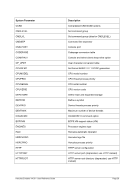
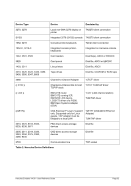
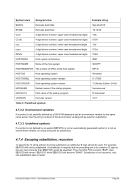
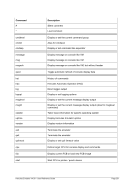
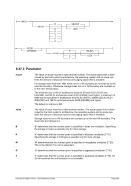
6.7.2 Syntax
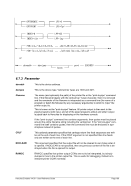
Descriptive
filename [RAWCC] [
[ lpi idx lpp
[1
or
[]port
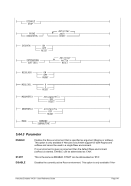
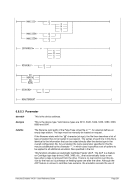
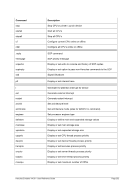
Diagram
Êʬ¬¬ ¬¬¬ ¬¬¬ filename ¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬Ê
ʬ¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬§¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬§¬¬¬¦¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¦¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬¬Ê
RAWCC