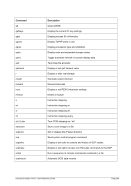
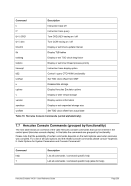
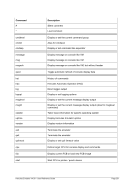
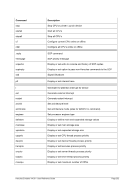
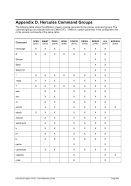
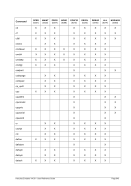
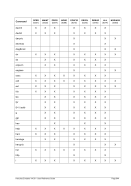
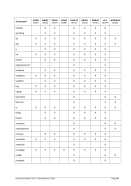
FCBCHECK
This argument specifies that an attempt to skip to a FCB channel for which no line
number has been set will cause the command to be rejected with a unit check. This
is the default.
NOFCBCHECK
This argument specifies that an attempt to skip to a FCB channel for which no line
number has been set will cause the next line of output printed on the next line on
the printer output. The opposite, FCBCHECK, is the default.
OPTBROWSE
Printing is optimized for browsing. This is the default.
OPTPRINT
Printing is optimized for printed output.
LPI=
Specifies the number of lines per inch. The value of lpi must be 6 or 8. The default
number of lines per inch is 6.
INDEX=
Sets the 3211 indexing. The value of idx must be in the range of 0 - 31. The default
is 0.
LPP=
Specifies the number of lines per page. The value of lpp must be numeric but is not
further checked. Any number of lines per page is allowed. The default number of
lines per page is 66.
FCB=
FCB specifies an initial FCB image to use for the printer. The argument must be
given in the form l1:c1, ... ,l12:c12 where 'l' and 'c' are numeric. 'l' is the line number
and 'c' is the assigned channel. There is a maximum of 12' l:c' pairs allowed.
The default is FCB=1:1,07:2,13:3,19:4,25:5,31:6,37:7,43:8,61:9,49:10,55:11,61:12.
host
This is the hostname or the IP address of the socket device.
port
This is the port number of the socket device.
SOCKDEV
SOCKDEV indicates that the line printer is a socket device wherein the filename is
actually a socket specification instead of a device filename.
When used, there must only be one filename specified in the form port or host:port.
The device then accepts remote connections on the given TCP/IP port and writes
data to the socket instead to a device file.
This allows automatic remote spooling of line printer data. The sockdev option is
mutually exclusive with all other printer options (like CRLF etc.) and must be speci-
fied alone.
6.7.4 Examples
Example 1:
Define a 1403 line printer device on device address 000E. The printed output has to be written to the file
"D:\PRT\PRT1.TXT" with carriage return line feed sequences at the end of each line. Any existing output
in the file has to be kept when the file is opened for output.
000E 1403 D:/PRT/PRT1.TXT CRLF NOCLEAR