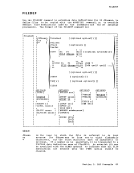
2 • 3. RENAME If you code an equal sign (=) in an output fileid in
corresponding to an asterisk in an input fileid, all
satisfy the condition are renamed. For example:
a position
files that
rename* assemble a = oldasm =
renames all files
filetype ofOLDASM. with a filetype of ASSEMBLE to
Current filenames are retained.
files with aYou cannot use the
another.You must
filemode letters.
RENAME command to move a file from one disk to
use theCOPYFILE com mana if you want to change You can use the RENAME command to modify filemode numbers, for
example,
rename * module al = = a2
changes the filemode number on allMODULE files that have a mode
number of 1 to a mode number of 2.You can invoke the RENAME command from the terminal, from an EXEC file, or as a function from a program. If
a function or from an EXEC file that has the&CONTROL NOMSG option
in effect, the messageDMSRNM002E FILE 'fn ft fm' NOT FOUND is not
issued.
Normally, the master file directory for
whenever you issue a command that affectsyou use the NOUPDIRT option of the RENAME directory is not updated until you issue
updates, or deletes any file on the disk,
a
files on the disk.When command, the master file
a commana that writes,
or until you explicitly
release the disk(with the RELEASE command; • newfn newft newfm
The new filename, filetype, and filemode of each file altered is
displayed when theTYPE option is specified and an asterisk was specified for at least one of the file identifiers (fn, ft or fm)
of the input fileid.DMSRNM002E FILE 'fn ft fm' NOT FOUND RC=28 DMSRNM003E INVALID OPTION 'option' RC=24 DMSRNM019E IDENTICAL FILEIDS RC=24 DMSRNM024E FILE 'fn ft fm' ALREADY EXISTS RC=28 DMSRNM030E FILE 'fn ft fm' ALREADY ACTIVE RC=28 DMSRNM037E DISK 'mode (cuu) , IS READ/ONLY RC=36 DMSRNM048E INVALID FILE MODE 'fm' RC=24 DMSRNM051E INVALID MODE CHANGE RC=24 DMSRNM054E INCOMPLETE FILEID SPECIFIED RC=24 DMSRNM062E INVALID * IN OUTPUT FILEID RC=20 , I Section 2. CMS Commands 161
corresponding to an asterisk in an input fileid, all
satisfy the condition are renamed. For example:
a position
files that
rename
renames all files
filetype of
Current filenames are retained.
files with a
another.
filemode letters.
RENAME command to move a file from one disk to
use the
example,
rename * module al = = a2
changes the filemode number on all
number of 1 to a mode number of 2.
a function or from an EXEC file that has the
in effect, the message
issued.
Normally, the master file directory for
whenever you issue a command that affects
updates, or deletes any file on the disk,
a
files on the disk.
a commana that writes,
or until you explicitly
release the disk
The new filename, filetype, and filemode of each file altered is
displayed when the
of the input fileid.