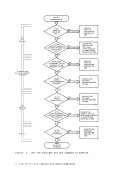
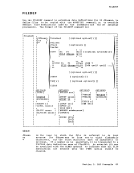
CLEAR
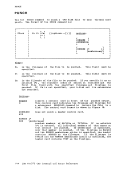
DLBL
removes any existing definitions for the specified ddname.
Clearing a ddname before defining it ensures that a file
definition does not exist and that any options previously
defined with that ddname no longer have any effect.and the file identifier (fn
ft) that follows is aCMS filename and filetype.
FILE ddname is the defaultCMS file identifier associated with
allnon-CMS data sets. (See Usage Note 3 for CMS/DOS users.) DSN indicates that this is a non-CMS file.
? indicates that you are going to enter the data set name
interactively. When prompted, you enter the data set name or
fileid in its exactform, including embedjed blanks, hyphens,
or periods.quaIl [quaI2 •.• qualn] Sy Sxx: x
PERM
is an as data set name orDOS file-ide Only data sets named
according to standard as conventions may be entered this way;you must omit the periods between qualifiers. (See Usa.ge Note
2. )(CMS/DOS only.) indicates the system or programmer logical
unit that is associated with the disk on which the disk
file resides. The logical unit must have been previously
assigned with theASSGN command. If a DLBL definition is
already in effect for the specified ddname,SYSxxx may be
omitted; otherwise, it is required.
indicates that this DLBL definition can be cleared only
with an explicit CLEAR request. It willnot be cleared
when the DLBL * CLEAR command line is entered.
All DLBL definitions, including those entered with thePERM option, are cleared as a result of a program abend or HI
(halt execution) Immediate command.
be
overridden and new options merged into theold definition.
Both the ddname and the file identifier must be the same in
order for the definitions to be merged.NOCHANGE does not alter any existing DLBL definition for the
specified ddname, but creates a definition if none existed.VSAM indicates that the file is a VSAM data set. This option
must be specified forVSAM functions unless the EXTENT, MULT, CAT, or BUFSP options are entered or the ddnames IJSYSCT or IJSYSUC are used. EXTENT indicates that you are going to use access method services
to define aVSAM catalog, data space, or unique cluster and
you want to enter extent information.MULT indicates that you are going to reference an existing
multivolume data set and you want to enter the volume
specifica tions.Section 2. CMS Commands 61
DLBL
removes any existing definitions for the specified ddname.
Clearing a ddname before defining it ensures that a file
definition does not exist and that any options previously
defined with that ddname no longer have any effect.
ft) that follows is a
FILE ddname is the default
all
? indicates that you are going to enter the data set name
interactively. When prompted, you enter the data set name or
fileid in its exact
or periods.
PERM
is an as data set name or
according to standard as conventions may be entered this way;
2. )
unit that is associated with the disk on which the disk
file resides. The logical unit must have been previously
assigned with the
already in effect for the specified ddname,
omitted; otherwise, it is required.
indicates that this DLBL definition can be cleared only
with an explicit CLEAR request. It will
when the DLBL * CLEAR command line is entered.
All DLBL definitions, including those entered with the
(halt execution) Immediate command.
be
overridden and new options merged into the
Both the ddname and the file identifier must be the same in
order for the definitions to be merged.
specified ddname, but creates a definition if none existed.
must be specified for
to define a
you want to enter extent information.
multivolume data set and you want to enter the volume
specifica tions.