specified character "a" for all xx characters displayed at the
terminal.
returns all characters to their default translation.
the SCRIPT command output is directed to the terminal,
mode.
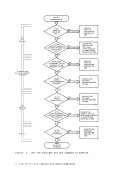
accepts svstem and user abbreviations for system
available.
accepts only the full system command name or the full user
synonym (if one is available) for system commands.
For a discussion of the relationship of the
types
with the appropriate terminal feature and a two-color ribbon.
Supported terminals are described in the
treats
the filename of the
does not consider
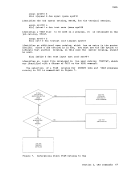
passes command names that
is, unknown commands are considered to be
generates an error message at the terminal if a command is not
recognized by
after command execution.
nonbuffered terminals.
the default
specifies that you do not want a console read to be issued
until you press the Enter key or its
default for display terminals because the display terminal
does not lock, even when there is no READ active for it.