location in the
location that is branched to. The format of the
is:
r
TOP
line-number transfers control to a specific line in the
-label transfers control to a specific label in the
label must begin with dash (-), and it must be the first
token on a line. The remainder of the line
executable statement or it may be null.
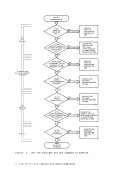
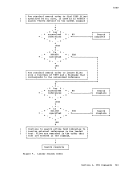
1. Scanning for an
file, and (if unsuccessful) ends on the line above the
label, the first one encountered by these rules satisfies the
search.
2. To provide a branch up or down a specific number of lines in the
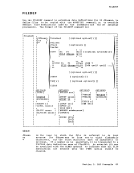
&HEX
conversion in an
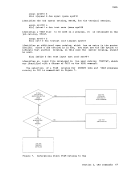
r
statement to initiate or
procedure. The format of
inhibit hexadecimal
the
-----------,
interpreted as hexadecimal notation.