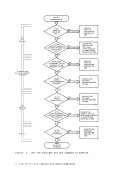
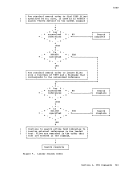
programmer logical unit for a virtual
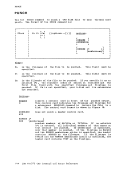
IGN
TJA
(options
-----,
1
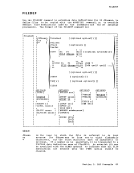
specifies the system or programmer logical unit to be assigned
to a particular physical device.
valid programmer logical units in
assigned to any valid device. The system logical units you
are:
Reader,disk,tape
Reader,disk,tape
Punch,disk,tape
Printer,disk,tape
Terminal,printer
Tape
Disk
Disk
Disk
Disk
The assignment of a system logical unit to a particular device
the file in
is the spooled card reader (card reader
blocked)
drive. It is either 1, 2, 3, or 4, representing virtual
addresses 181, 182, 183, and 184, respectively. If n is
omitted,
mode specifies the one-character mode letter
assigned to the logical unit
of the disk being
The disk must be