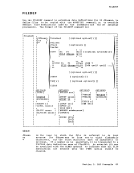
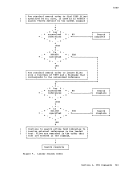
For those portions of the file identifier that you want
same, you may code an equal sign in the output fileid.
command line above can be entered:
coPvfile test1 assemble a test2 = =COPYFILE to stay the
Thus, the
The equal signmay be used as a prefix or suffix of a file
identifier. For example, the command:
copvfile abc file= type= =
creates an output file called FILEATYPEB C. When you copy a file from one
the old and new filemodes, and any
to make; for example:virtual disk to another, you specify
filename or filetype change you want
copvfile test3 assemble c good = a
This command makes a copy of the file TEST3GOOD
If you want to copyonly particular records in a file, you can use
thePRLABEL/TOLABEL options. Por example:
copvfile old test anew test a (frlabel start for 41 copies 41 records from the file OLD TEST Al, beginning with the record
beginning with the character string START into the fileNEW TEST 11. You can combine two or more files into a single file with the COPYFILE command. For example: copyfile test datal a test data2 = test data3 b
copies the files TEST DATAl and TEST DATA2 from your A-disk and combines
them into a file, TEST DATA3, on your B-disk.
Note that if any input file has a filemode number of 3, itis possible that the file will be copied in a sequence different from its
order on the disk.
If you want to combine two more files without creating a new file:
use theAPPEND option. Por example:
copyfile new list a old list a (append
appends the fileNEW LIST A to the bottom of the existing file labeled OLD LIST A.
Note: If the fileNEW LIST A has a different LRECL from the file OLD LIST A, the appended data is padded, or truncated
6 to the LRECL of the file OLD LIST A.
Whenever you code an asterisk (*) in an input fileid, you may cause
one or more files to be copied, depending upon the number of files that
satisfy the remaining conditions. For example:
copyfile * test a combined test a
copies all files with a filetype of TEST on your A-disk into a single
file namedonly one file with a filetype of TEST
exists, only that file is copied.
Section 2.CKS Commands 39
same, you may code an equal sign in the output fileid.
command line above can be entered:
coPvfile test1 assemble a test2 = =
Thus, the
The equal sign
identifier. For example, the command:
copvfile abc file= type= =
creates an output file called FILEA
the old and new filemodes, and any
to make; for example:
filename or filetype change you want
copvfile test3 assemble c good = a
This command makes a copy of the file TEST3
If you want to copy
the
copvfile old test a
beginning with the character string START into the file
copies the files TEST DATAl and TEST DATA2 from your A-disk and combines
them into a file, TEST DATA3, on your B-disk.
Note that if any input file has a filemode number of 3, it
order on the disk.
If you want to combine two more files without creating a new file:
use the
copyfile new list a old list a (append
appends the file
Note: If the file
6
Whenever you code an asterisk (*) in an input fileid, you may cause
one or more files to be copied, depending upon the number of files that
satisfy the remaining conditions. For example:
copyfile * test a combined test a
copies all files with a filetype of TEST on your A-disk into a single
file named
exists, only that file is copied.
Section 2.