DLBL
DLBLUse the DLBL command: • In CMS/DOS, to define DOS and CMS sequential disk files for program
input/output; to identifyDOS files and libraries; to define and
identifyVSAM catalogs, clusters, and data spaces; and to identify VSAM, DOS, or CMS files used for VSAM program input/output and access
method services functions.• In eMS, to define and identify VSAM catalogs, clusters, and data
spaces; to identifyVSAM files used for program input/output; and to
identify input/output files forAMSERV. The format of the DLBL command is:
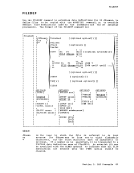
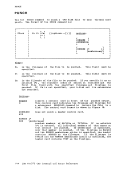
r-, I I r r 1 1 I DLBL Iddname {mode} ICMS fn ft 1 [ (optionA optionB [) ]] 1 , , DUt1t1Y 1£t1S I I I , L J
1I I I , I r ,
1I , ddna me
{moae}'DSN quaIl [ qua12 ••• qualn ] I I I I DUMMY IDSN ? , 1 I I L .J , , I [ (option A optionB optionC [) ]] I I I " I Iddname CLEAR " I I * " I L J , I QEiiQn!: QEtiQnB: , 1 [ SYSxxx] [ PERM] [ VSAM ] , I r ,
r 1, I I£HANGE I IEXTENTI , 1 INOCHANGEI ,MULT I I I L .J L .J , I [CAT catdd] , , [BUFSP nnnnnn] , L --' NQi§: The operands and options of the DLBL command are described below. Usage notes are provided for general usage, followed by additional notes
forCMS/DOS users, and then additional notes for as VSAt1 users.
ddname
modeDUMMY specifies a one-to seven-character program ddname (OS) or
filename(DOS), or dname (as specified in the FILE parameter
of an access method services control statement). An asterisk
(*) entered with theCLEAR operand indicates that all DLBL
definitions, except those that are entered with the PERM
option, are to be cleared.
specifies a validCMS disk mode letter and
filemode number.A letter must be specified; if
not specified, it defaults to 1. The disk must
when the DLBL command is issued.
optionally,
a number is
be accessed
specifies that no realI/O is to be performed. A read
operation results in an end-of-file condition and a write
operation results in a successful return code.DUMMY should
not be used forOS VSAM data sets (see Usage Note 3). 60 IE! eMS Command and Macro Reference
DLBL
input/output; to identify
identify
method services functions.
spaces; to identify
identify input/output files for
r
1
1
{moae
r 1
for
ddname
mode
filename
of an access method services control statement). An asterisk
(*) entered with the
definitions, except those that are entered with the PERM
option, are to be cleared.
specifies a valid
filemode number.
not specified, it defaults to 1. The disk must
when the DLBL command is issued.
optionally,
a number is
be accessed
specifies that no real
operation results in an end-of-file condition and a write
operation results in a successful return code.
not be used for