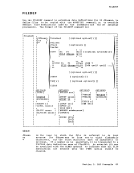
DLBL
1.You must use the DLBL command to identify all access method
services input and output files, and to identify allVSAM input and
output files referenced in programs.For all other file definitions, including os or :MS disk files
referenced in programs that useVSAM data management, you must use
the FILEDEF command.
2. A DLBL ddname may have a maximum of seven characters. If you have
ddnames in your programs that are eight characters long, only the
first seven characters are processed when the programs are executed
inCMS. If you have two ddnames with the same first seven
characters and you attempt to execute this program ineMS, you will
receive an open error when the second file is opened.You should
recompile these programs providing unique seven-character ddnames.
3. If you release a disk for which you have a DLBL definition in
effect, you should clear the DLBL definition before you execute aVSAM program or an AMSERV command. CMS checks that all disks for
which there are DLBL definitions areaccesse1, and issues error
messageDMSSTT069E if any are not. You must specify extent information
when you use the access method services control statements DEFINESPA:E, DEFINE MASTERCA!ALOG, DEFINE USERCATALOG, DEFINE CLUSTER (UNIQUE); or
when you use theIMPORT or IMPORTRA functions for a unique file. Space allocation is made only for primary allocation amounts. When you enter the EXTENT option of the DLBL command, you are
promoted to enter the disk extents for the specified file.You must
enter extent information in accordance with the following rules:• You must specify the starting track number and number of tracks for
each10 38
Thisextent allocates 38 tracks, beginning with the 19th track, on a
3330 device.• All extents must begin and end on cylinder boundaries, regardless of
whether theAMSERV file contains extent information in terms of
cylinders, tracks, or records.• Multiple extent entries may be entered commas or on different lines. Commas
ignored.
on a single line separated by
at the end of a line are• Multiple extents for the same volume must be entered in numerically
ascending order; for example:20 400, 6 00 80 These extents are valid for a 2314 device. • When you enter multivolume extents, you must specify the mode letter
forextents on additional disks; extents for each disk must be
entered consecutively. For example:
68 IBM VM/37QCMS Command and Macro Reference
1.
services input and output files, and to identify all
output files referenced in programs.
referenced in programs that use
the FILEDEF command.
2. A DLBL ddname may have a maximum of seven characters. If you have
ddnames in your programs that are eight characters long, only the
first seven characters are processed when the programs are executed
in
characters and you attempt to execute this program in
receive an open error when the second file is opened.
recompile these programs providing unique seven-character ddnames.
3. If you release a disk for which you have a DLBL definition in
effect, you should clear the DLBL definition before you execute a
which there are DLBL definitions are
message
when you use the access method services control statements DEFINE
when you use the
promoted to enter the disk extents for the specified file.
enter extent information in accordance with the following rules:
each
This
3330 device.
whether the
cylinders, tracks, or records.
ignored.
on a single line separated by
at the end of a line are
ascending order; for example:
for
entered consecutively. For example:
68 IBM VM/37Q