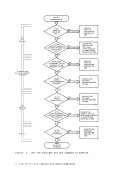
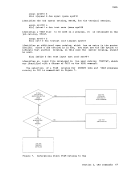
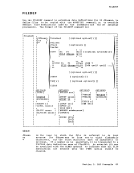
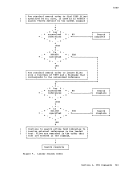
FILEDEF
retains the current definition until it either is
explicitly cleared or is changed with a new FILEDEF
command with the CHANGE option. If PERM is not
specified, the definition is cleared when a FILEDEF
*
CLEAR
already exists for a ddname and a new FILEDEF command
specifving the same ddname is issued; the options
associated with the two definitions are merged.
duplicated in the new definition.
to the option list.
retains the current file definition, if one exists, for
the specified ddname.
is the record format of the file, where "a" can be one of
the following:
F
FB
fixed blocked
1
va riable length
variable blocked
1
variable length, spanned records
machine print control codes
2
LRECL nnnnn is the logical record length (nnnnn) of the
restrictions.
BLKSIZE nnnnn
is the logical block size (nnnnn) of the
restrictions. If both
specified, the value of nnnnn for
If a
should specify RECFM FB
can be improved for
a multiple of
The maximum
file.
number of records (nnnnn) in the extent for the
The default is
be searched. The maximum value is 256.