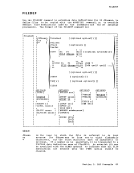
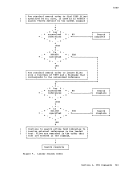
FILEDEF
1. If you do not issue a FILEDEF command for an os input or output
file,eMS uses the ddname on the DCB macro to issue the following
default file definition:
FILEDEF ddname DISK FILE ddname Al
See"Usage Notes" under the discussion of the ASSEMBLE command for
information on the default file definitions made by the assembler.
2. To identifyDOS files for DOS program execution or to identify VSAM data sets for either OS or DOS program execution, you must use the
DLBL command.
3. A file definition established with the FILEDEF command remains in
effect until explicitly changed or cleared. The system clears file
definitions under the• When the assembler or any of the language processors are
invoked. (Note that FILEDEF definitions entered with thePERM option are not cleared.) • When a program abends or when you issue the Immediate command HX
to halt command or program execution.4. The FILEDEF command does not supply default values for LRECL and
BLKSIZE. As underOS, if DCB information is unavailable when a
file is opened, an open error is issued for the file. The
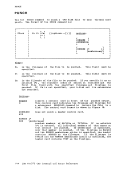
following chart summarizes the results atOPEN time, of specifying
LRECL and BLKSIZE options.r-- BLKSIZE Not
Specified
Specified
Not
Specified
SpecifiedL--- LRECL
Not
SpecifiedResults I , --------f IIf the input file exists on disk, the , litem length (or item length +4 for vari- , ,able-length records) becomes the BLKSIZE.I --------I Not ILRECL=BLKSIZE (or LRECL=BLKSIZE-4, for , Specified Ivariable-length records). Specified IBLKSIZE=LRECL (or BLKSIZE=LRECL+4, for Ivariable-length records) e Specified !The values specified are used. , , I _________________________________________________________ -J If V or VB is specified for RECFM, LRECL must be at least 4 bytes
less than BLKSIZE.DOS sequential (SAM) files do not contain BLKSIZE, LRECL, or RECFM specifications. These options must be specified by a FILEDEF
command or DCB statement ifOS macros are used to access DOS files. Otherwise the defaults, BLKSIZE=32760 and RECFM=U, are assumed.
LRECL is not used forRECFM=U files.
5. There is an auxiliary processing option for FILEDEF that is only
valid when FILEDEF is executed by an internal program call: this
option cannot be entered as a terminal command. The option,AUXPROC addr, allows an auxiliary processing routine to rece1ve
control duringI/O operations. For details on
option of the FILEDEF command, seeCMS Commands 93
1. If you do not issue a FILEDEF command for an os input or output
file,
default file definition:
FILEDEF ddname DISK FILE ddname Al
See
information on the default file definitions made by the assembler.
2. To identify
DLBL command.
3. A file definition established with the FILEDEF command remains in
effect until explicitly changed or cleared. The system clears file
definitions under the
invoked. (Note that FILEDEF definitions entered with the
to halt command or program execution.
BLKSIZE. As under
file is opened, an open error is issued for the file. The
following chart summarizes the results at
LRECL and BLKSIZE options.
Specified
Specified
Not
Specified
Specified
Not
Specified
less than BLKSIZE.
command or DCB statement if
LRECL is not used for
5. There is an auxiliary processing option for FILEDEF that is only
valid when FILEDEF is executed by an internal program call: this
option cannot be entered as a terminal command. The option,
control during
option of the FILEDEF command, see