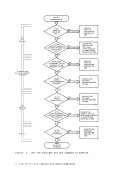
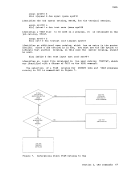
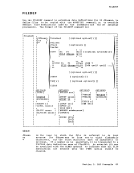
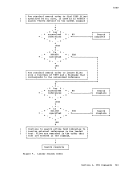
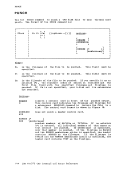
Edit Macros-$MOVE Use the $MOVE edit macro to move one or more lines from one place in a
file to another place. The format of the$MOVE macro is: .- , I $MOVF n {UP m } I I L
nDOWN m TO label
indicates the number of records you want to move, beginning
with the current line. The maximum number of lines you can
move is 25.UP m indicates that you want to move the lines toward the top of
the file, m lines above the current line.DOWN m TO label
indicates that you want to move the lines toward the end of
the file, m lines below the last line you are going to move.
indicates that you want the lines inserted
specified label. The label must be one to
characters and must start in column 1.
following the
eight uppercase
1. The last line moved becomes the new current line.
2. If the label is not found or if theDOWN value exceeds the number
of lines remaining before end of file, the lines are inserted at
the end of the file. If theUP value exceeds the number of lines
remaining before top of file, the lines are inserted at the top of
the file.
3. Ifyou use the logical line end symbol (#) to stack additional
subcommands on the same line with the$MJVE request, those
subcommands are cleared from the console stack and the message:STACKED LINES CLEARED BY $MOVE is displayed. The stacked subcommands are not executed.
4. Because it uses console functions,$MOVE will truncate duplicated
records containing binary zeros or nonprintable characters.
5. Because it uses theSTACK EDIT subcommand, $MOVE can move a maximum
of130 characters in one line. Longer lines are truncated. When verification is on, the last line moved is displayed.
Section 3. EDIT Subcommands and Macros 261
file to another place. The format of the
n
indicates the number of records you want to move, beginning
with the current line. The maximum number of lines you can
move is 25.
the file, m lines above the current line.
indicates that you want to move the lines toward the end of
the file, m lines below the last line you are going to move.
indicates that you want the lines inserted
specified label. The label must be one to
characters and must start in column 1.
following the
eight uppercase
1. The last line moved becomes the new current line.
2. If the label is not found or if the
of lines remaining before end of file, the lines are inserted at
the end of the file. If the
remaining before top of file, the lines are inserted at the top of
the file.
3. If
subcommands on the same line with the
subcommands are cleared from the console stack and the message:
4. Because it uses console functions,
records containing binary zeros or nonprintable characters.
5. Because it uses the
of
Section 3. EDIT Subcommands and Macros 261