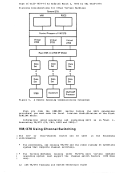
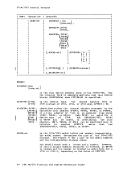
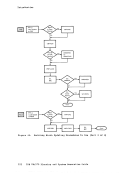
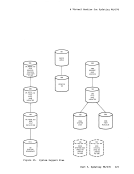
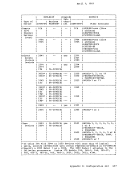
read-only and contains the
issue the
is entered or until you log off. The disk-resident modules are loaded
into virtual storage only when their services are needed.
The A-disk is a read/write disk and is the primary or first disk.
Files that you wish to retain for later use are stored on one of your
disks. Information stored on a disk remains there until you erase it.
An exception is the temporary disk; files written on this disk are lost
when you log off. In addition to the system disk
disk (A-disk), each
back to the terminal.
commands and input files
program results, and error
from the terminal and
and prompting messages
The virtual card reader is used as the input medium for files, source
decks, and data to be processed by your programs. The virtual card
punch is used for your output files, language processor object decks,
and various other types of data. The virtual printer is used for
program results, storage dumps and language processor output.
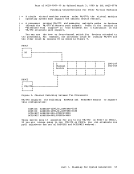
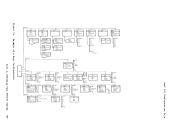
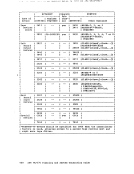
The following is an example of a
LINK
Directory program control statements are described in
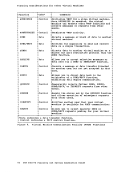
this entry describes the
minidisk at 191.
configuration and also the spooling classes of the unit record devices.
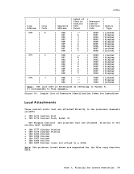
configuration as needed.
libraries)
Part 1. Planning for